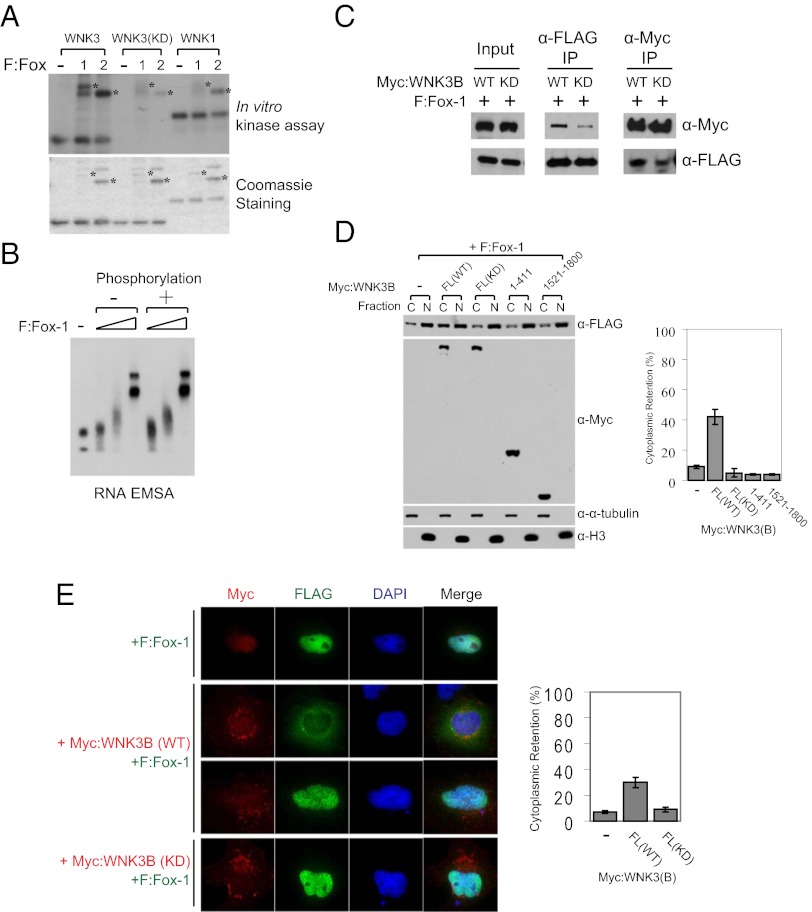
Fig. 4.
WNK3 modulates the subcellular localization of Fox-1 in a kinase activity-dependent manner. (A) In vitro kinase assay with purified WNK kinase domains and F:Fox-1 and F:Fox-2 (Upper). Following these reactions, Fox proteins contained ∼2 mol phosphate/mol protein. Coomassie blue staining of proteins used for the assay (Lower). Asterisks indicate positions of Fox proteins. (B) RNA electrophoretic mobility-shift assay with the RNA template including a UGCAUG element and nonphosphorylated or WNK3-phosphorylated F:Fox-1. Triangles represent increasing amounts (0.1, 0.3, and 1 μg) of proteins used. (C) Myc-tagged WNK3 proteins and F:Fox-1 were expressed in HEK293T cells for coimmunoprecipitation. (D) F:Fox-1 was coexpressed with Myc-tagged WNK3 proteins in HEK293T cells and then subjected to subcellular fractionation as described in Experimental Procedures. C and N represent cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, respectively. Alpha-tubulin and histone 3 (H3) were detected as markers of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, respectively. To calculate the percentage of cytoplasmic retention, the cytoplasmic F:Fox-1 intensity was divided by the total intensity of both fractions and multiplied by 100 (mean ± SD). (E) Immunostaining of F:Fox-1 (green), Myc:WNK3 (red), and DAPI (blue). HeLa cells were transfected for 60 h as indicated. Cytoplasmic and nuclear intensities were quantitated individually through ImageJ and calculated as described in D.