Fig. 4.
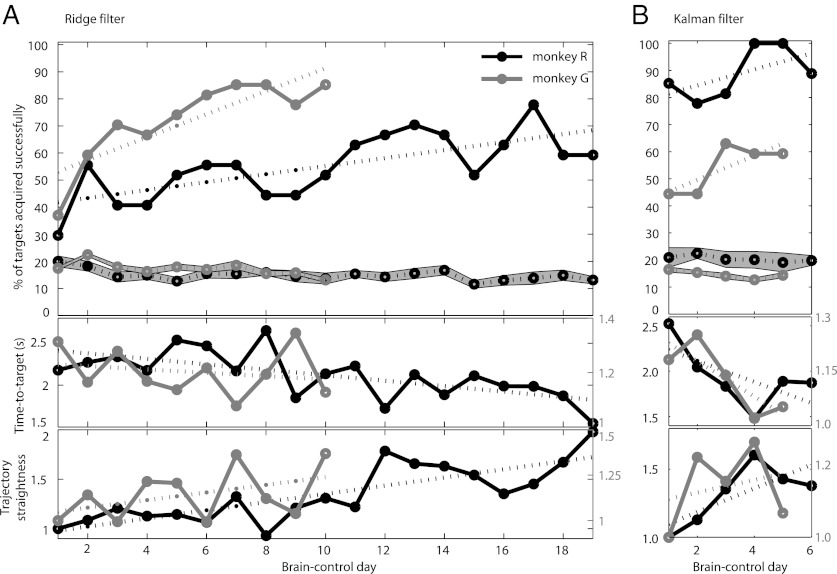
Learning brain-control. Improving behavioral performance in both monkeys for consecutive brain-control days shows that the monkeys learned to use PPC spike activity driving the decoding algorithm to direct cursor movement. Top graphs show daily success rates and chance performance ± SD (gray band) for ridge (A) and Kalman filter decode (B). Middle graphs show time-to-target for successful reaches. Bottom graphs show trajectory straightness. The trajectory straightness describes the ratio of the shortest (straight) distance from initial cursor location to target location and the actual distance the cursor traveled during the target acquisition, i.e., increasing straightness values indicate more direct trajectories. The trajectory straightness was normalized for first-day performance.