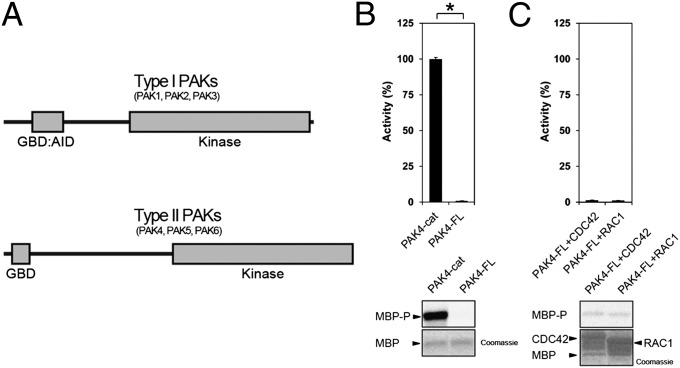
Fig. 1.
PAK schematic and kinase assays for type II PAKs. (A) Schematic diagram for type I and type II PAK family members. The type I PAKs contain an N-terminal GBD that overlaps with an AID (GBD:AID), and a C-terminal kinase domain. The type II PAKs contain an N-terminal GBD and a C-terminal kinase domain. All PAKs contain proline-rich patches between the N-terminal GBD and C-terminal kinase domains. (B) Kinase assay for PAK4-cat and PAK4-FL. Purified PAK4 catalytic domain PAK4-cat135–426 (PAK4-cat and PAK4-FL were assayed for activity toward MBP with [γ-33P]ATP. Reactions were subjected to SDS/PAGE, exposed to phosphor storage screen, scanned, and MBP phosphorylation quantified by optical densitometry (Lower, MBP-P). MBP loading is shown (Lower, MBP, Coomassie). Activities are shown as a percentage of PAK4-cat activity (100%). PAK4-FL displays ∼100-fold less activity than PAK4-cat. *P < 0.01, t test. (C) GTPases do not increase PAK4-FL catalytic activity. PAK4-FL kinase activity toward MBP was assayed in the presence of either purified CDC42 or RAC1 with GMP-PNP and Mg2+. MBP and GTPase loading are shown. Small GTPases do not impact kinase activity of PAK4-FL toward MBP.