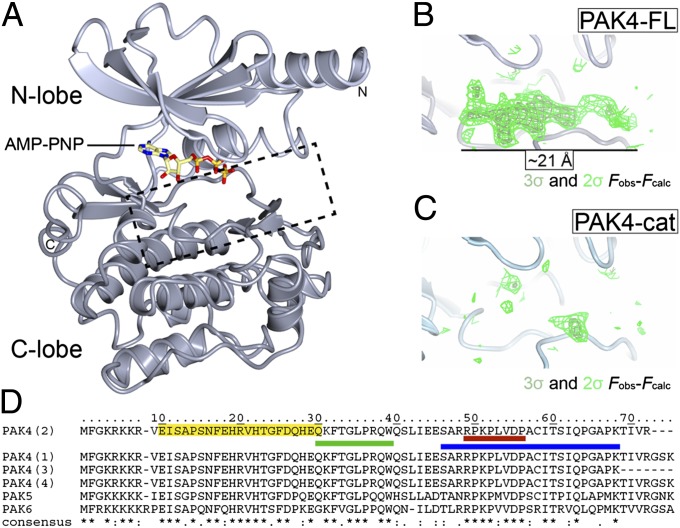
Fig. 2.
Structures of PAK4-cat and PAK4-FL in the P3 crystal form. (A) Overall structure of the PAK4 kinase domain. PAK4 kinase domain shown in ribbon format with N-lobe (light gray) and C-lobe (dark gray) indicated. Bound AMP-PNP shown in stick format. N and C termini are indicated. Region shown in B and C is indicted by a dashed box. (B and C) The PAK4-FL P3 crystal contains a significant region of positive difference electron density in the peptide substrate binding site; this is not observed in the PAK4-cat structure. Two contour levels (2σ and 3σ in dark and light green, respectively) are shown for the unbiased Fobs-Fcalc map. (D) Sequence alignment for the N terminus of human type II PAKs (UniProt accession nos: PAK4, O96013; PAK5, Q9P286; PAK6, Q9NQU5). The four PAK4 isoforms are shown, which are identical between the N terminus and residue K68. (*) indicates identical; (:), highly conserved; (.), semiconserved. The PAK4 GBD (CRIB) domain as defined by Abo et al. (5) is shaded yellow. QKF peptide, green; RPK peptide, red; and 23-mer peptide, blue.