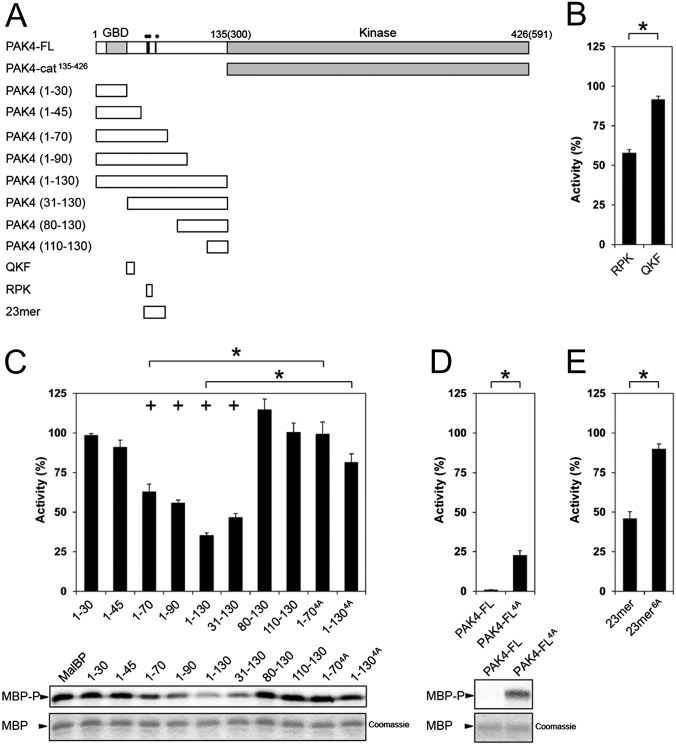
Fig. 3.
PAK4 kinase assays. (A) Schematic of constructs used for PAK4 kinase activity assays. Residues mutated are indicated on PAK4-FL as black lines with two filled circles (••) indicating R49PKP to A49AAA or a single filled circle (•) indicating I59T to A59A. (B) Purified PAK4 catalytic domain PAK4-cat135–426 (PAK4-cat) was assayed for activity toward MBP in the presence of RPK or QKF peptides. Radiolabel incorporation into MBP was determined by optical densitometry following SDS/PAGE and exposure to a phosphor storage screen. Activities are shown as a percentage of the activity of PAK4-cat135–426. For all, kinase assays show SEM for more than three experiments. RPK peptide significantly inhibits kinase activity. *P < 0.01, t test. (C) PAK4-cat135–426 activity in the presence of N-terminal constructs of PAK4. Purified MalBP fusion constructs PAK41–30, PAK41–45, PAK41–70, PAK41–90, PAK41–130, PAK431–130, PAK480–130, and PAK4110–130 were added and compared with addition of MalBP alone (MalBP). PAK41–70, PAK41–90, PAK41–130, and PAK431–130 inhibit kinase activity of PAK4-cat135–426. MBP phosphorylation (Lower, MBP-P) and loading are shown (Lower, MBP, Coomassie). Mutation of R49PKP to A49AAA in either PAK41–70 or PAK41–130 results in a loss of inhibition of kinase activity. Activities are shown as a percentage of the activity of PAK4-cat135–426 with negative control MalBP added. *P < 0.01, t test; +P < 0.01 by t test compared with PAK4-cat135–426 with MalBP alone. (D) Mutation of PAK4-FL restores kinase activity. Purified PAK4-FL containing point mutations R49PKP to A49AAA (PAK4-FL4A) show a significant increase kinase activity with respect to MBP. Activities are shown as a percentage of PAK4-cat135–426 activity. (E) Effect of 23-mer peptide on PAK4-cat135–426 kinase activity. The 23-mer peptide inhibits kinase activity better than the RPK peptide (B). Mutation of R49PKP to A49AAA and I59T to A59A in this peptide (23-mer6A) results in a loss of kinase inhibition. Activities are shown as a percentage of the activity of PAK4-cat135–426.