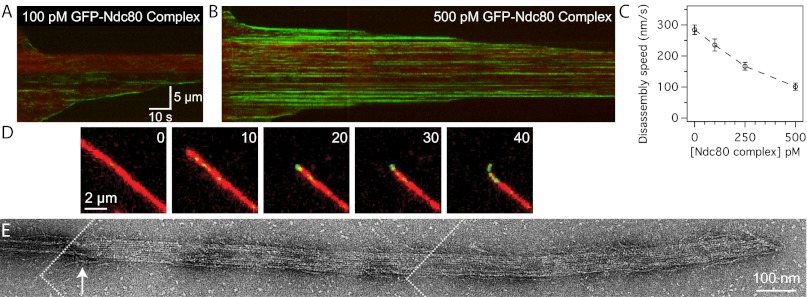
Fig. 2.
The Ndc80 complex slows microtubule disassembly and stabilizes protofilament extensions. Kymographs of disassembling microtubules (red) in the presence of (A) 100 pM or (B) 500 pM GFP-tagged Ndc80 complex (green). Brightness and contrast were adjusted equally in A and B. (C) Mean disassembly speeds ± SEM for microtubules in the presence of increasing concentrations of Ndc80 complex (without Ndc80 complex, n = 80; 100 pM Ndc80 complex, n = 31; 250 pM, n = 29; 500 pM, n = 34). (D) Time-lapse images of a disassembling microtubule (red) in the presence of 500 pM GFP-tagged Ndc80 complex (green) as a curled extension formed at the tip. Inset numbers show elapsed time, in seconds. See Fig. S3B for a gallery of images showing curled extensions. (E) Negative-stain electron micrograph of a disassembling microtubule tip (see SI Materials and Methods) stabilized by the Ndc80 complex. An arrow marks the transition from a closed microtubule to an open sheet. The figure was constructed from three images, the boundaries of which are depicted by dotted white lines.