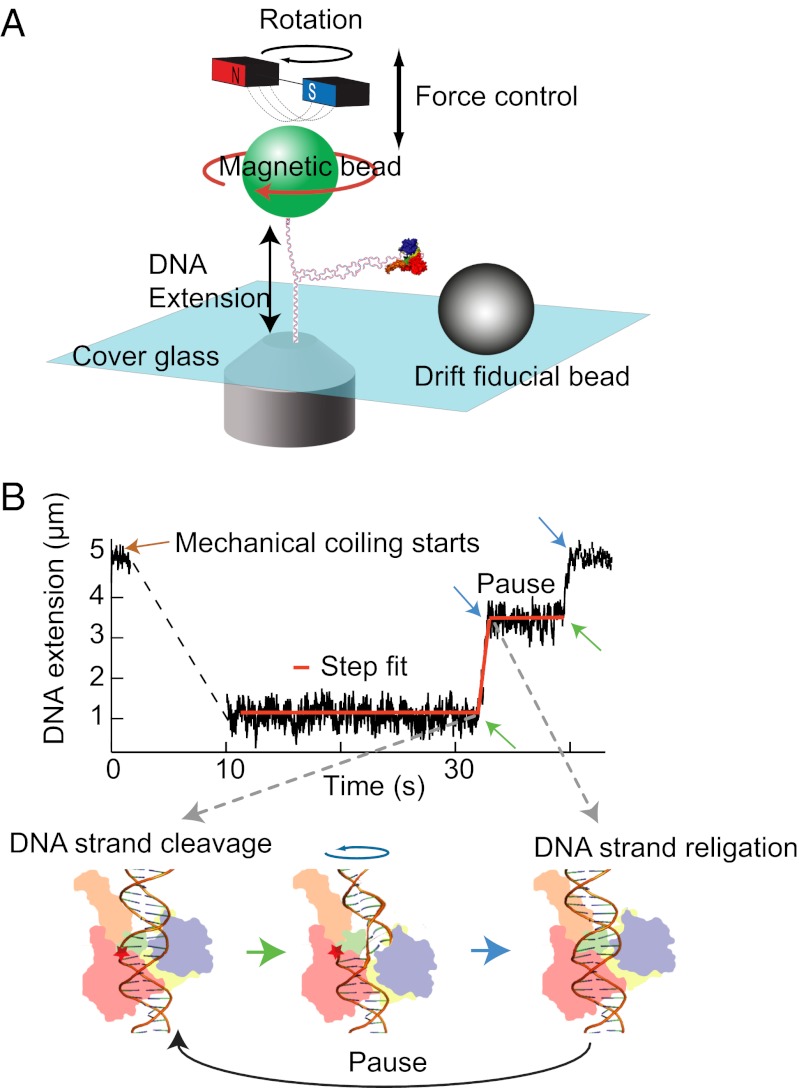
Fig. 1.
Cartoon of experimental setup (not to scale) and an example trace. (A) A DNA molecule is attached between the cover glass of a flow cell and a magnetic bead (green). Force is controlled by moving the magnet assembly above the flow cell. Rotating the magnetic bead by turning the magnets twists the DNA and generates supercoils. (B) DNA extension as a function of time and step-finding fit. DNA extension traces were fitted with a custom written step-finding routine based on a t test algorithm (40). The fitting routine extracts the extension change, duration, and linear velocity for each relaxation event and the duration of pauses between events. These phases of motion correspond to cleavage (green arrow), relaxation, and religation (blue arrow) depicted in the cartoon of Top1B enzyme bound to DNA.