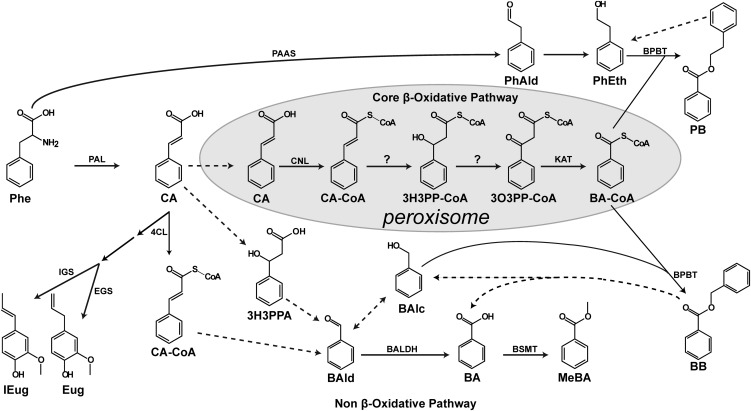
Fig. 1.
The benzoic acid biosynthetic network in plants. Solid arrows show established biochemical reactions, and dashed arrows depict possible steps not yet identified. Stacked arrows show the involvement of multiple enzymatic steps. The CoA-dependent β-oxidative pathway leading to BA-CoA formation is localized in peroxisomes and shown with a gray background. The proposed routes of the non–β-oxidative pathway in cytosol are also depicted. BA-CoA, benzoyl-CoA; BAlc, benzylalcohol; BAld, benzaldehyde; BALDH, benzaldehyde dehydrogenase; BB, benzylbenzoate; BPBT, benzoyl-CoA:benzylalcohol/2-phenylethanol benzoyltransferase; BSMT, benzoic acid/salicylic acid carboxyl methyltransferase; CA, cinnamic acid; CA-CoA, cinnamoyl-CoA; 4CL, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase; Eug, eugenol; EGS, eugenol synthase; IEug, isoeugenol; IGS, isoeugenol synthase; 3H3PPA, 3-hydroxy-3-phenylpropionic acid; 3H3PP-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-phenylpropanoyl-CoA; KAT, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase; MeBA, methylbenzoate; 3O3PP-CoA, 3-oxo-3-phenylpropanoyl-CoA; PAAS, phenylacetaldehyde synthase; PEB, phenylethylbenzoate; PhAld, phenylacetaldehyde; and PhEth, 2-phenylethanol.