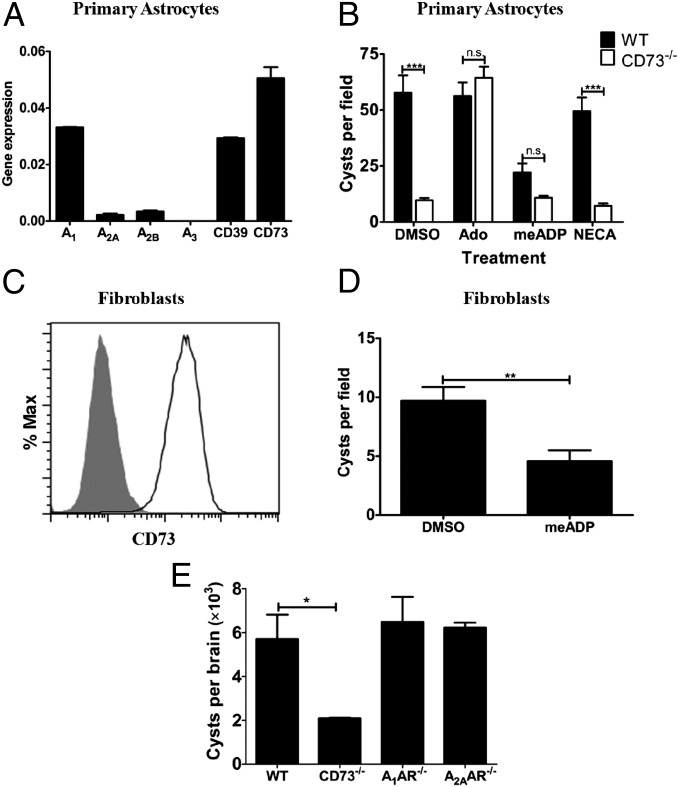
Fig. 5.
Exogenous adenosine rescues T. gondii cyst formation in CD73-deficient host cells independent of adenosine receptor signaling. (A) Gene expression analysis of adenosine receptors (A1, A2A, A2B, A3), CD39, and CD73 on cultured astrocytes. Real-time quantitative PCR results are normalized to the housekeeping gene PGK1. (B) Astrocytes from WT and CD73−/− neonates were cultured and infected with T. gondii tachyzoites of the ME49 strain in the presence or absence of adenosine (50 μM), the broad-spectrum adenosine receptor agonist NECA (10 μM), or the CD73 inhibitor meADP (50 μM). Cyst formation was assessed 12 d after continuous culture at pH 8.0 by immunofluorescence microscopy to quantify DBA binding cysts. (C) The human foreskin fibroblast line Hs27 was assessed for CD73 expression by flow cytometry (unshaded curve, CD73-PE-labeled cells; shaded curve, unstained live cells). (D) Cyst formation was quantified as described above following 8-d culture of T. gondii-infected Hs27 fibroblasts at pH 8.0 in the presence of DMSO or 50 μM meADP. Significant differences based on two-tailed t tests are displayed (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (E) Quantitation of brain parasite cyst burden in A1AR−/−, A2AAR−/−, CD73−/−, and WT mice infected with 20 cysts of T. gondii ME49 for 30 d (*P < 0.05).