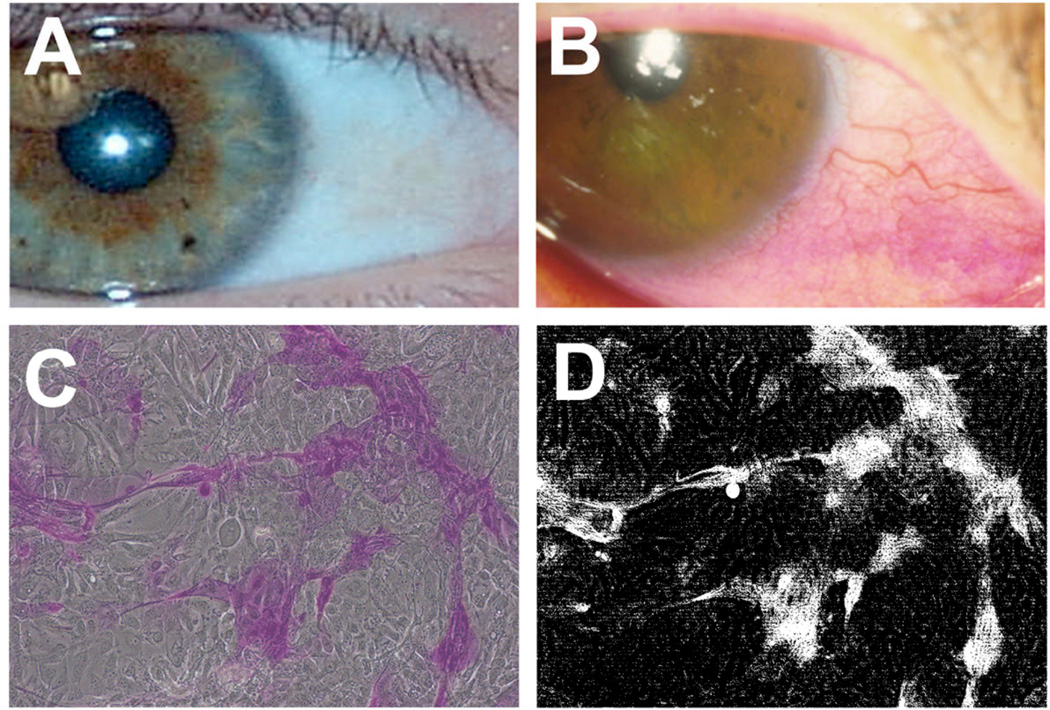
Fig. 1.
Rose bengal is an organic anionic dye used to assess damage to the ocular surface epithelium in ocular surface disease. Application of rose bengal onto the ocular surface results in patches of superficial punctate staining in patients with epithelial damage (B), but not in normal subjects (A). In culture, human corneal epithelial cells grown in stratification media contain areas of stratified cells that exclude the rose bengal dye (C). The amount of rose bengal uptake can be determined using ImageJ software (D) as described in step 3.4.7.