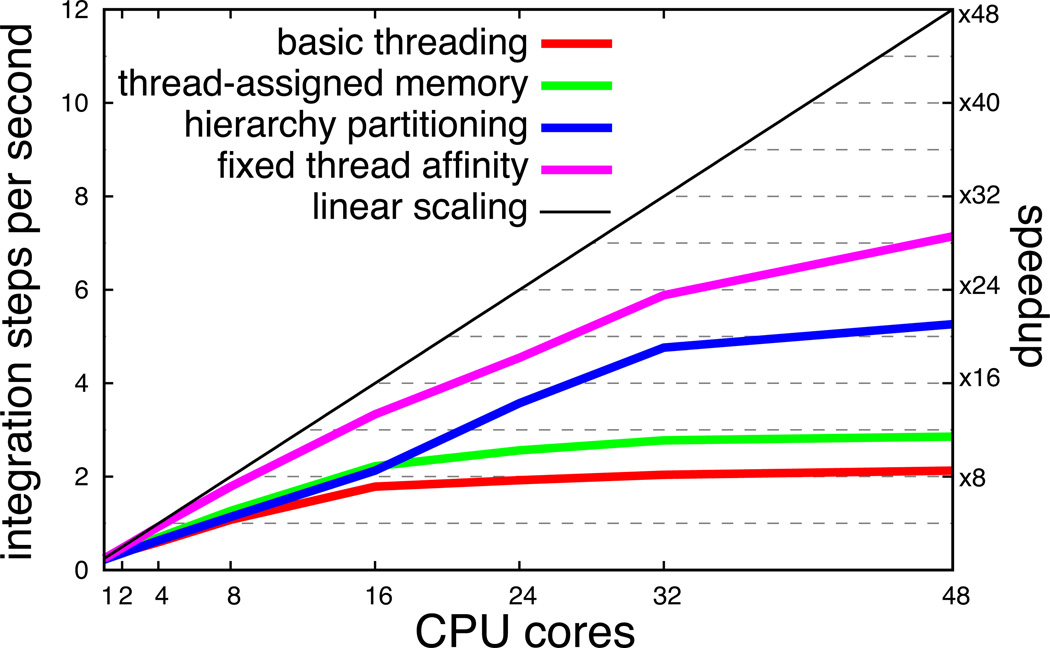
Figure 7.
Parallel scaling of PHI on a 48-core AMD Magny-Cours shared-memory computer running Linux. The system employed for benchmarking is the set of 18 pigments in the B850 ring of LH2 with LT = 4 and K = 1. Note that increasing the number of Matsubara frequencies K results in a dramatic reduction in performance of PHI. “Basic partitioning” refers to a cyclic partitioning of ADMs and the memory for all ADMs being assigned to a consecutive block; “thread-assigned memory” refers to instructing each thread to perform memory assignment for its set of ADMs in the cycling partitioning scheme; “hierarchy partitioning” refers to employing the partitioning described in Listings 1 and 2 and using thread-assigned memory; “fixed thread affinity” refers to employing the partitioning scheme in Listings 1 and 2, using thread-assigned memory and instructing the operating system’s thread scheduler to affix each thread to a particular processor such that no thread migration occurs.