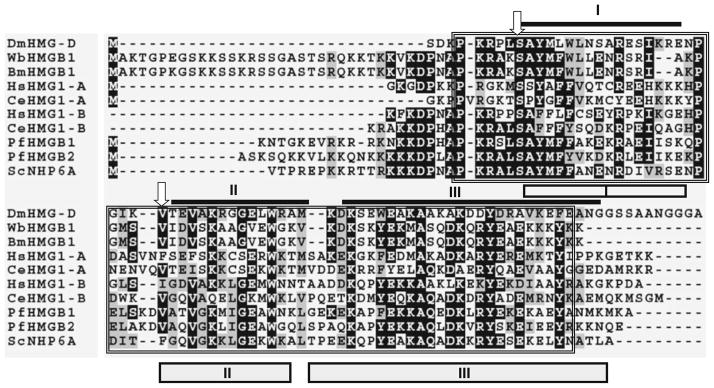
Fig. 1.
Multiple sequence alignment of HMGB 1 of W. bancrofti and B. malayi with HMG proteins from other parasitic organisms. HMG box domains were identified using PROSITE and marked by a box and compared with sequences of human, Saccharomyces NHP6A, and Drosophila HMG-D. Identical residues are represented as asterisks. Amino acids marked by arrows are two crucial determinants that differ between sequence-specific and the non-specific HMG domains. As shown here, a serine and a hydrophobic residue are present in all non-sequence or structural specific HMG proteins, whereas an asparagine and a hydrophilic residue are present at these positions of all sequence-specific HMG proteins. I, II, and III represent the three α-helices of the Drosophila HMG-D [dark lines (Murphy et al. 1999)] and Saccharomyces structure NHP6A [boxes (Allain et al. 1999)]