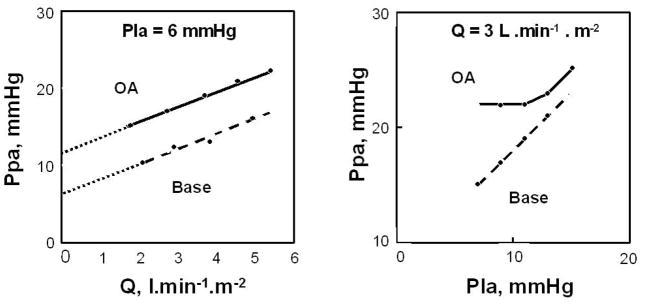
Figure 2.
Mean pulmonary artery pressure (Ppa) as a function of cardiac output (Q) at constant left atrial pressure (Pla), left panel, and Ppa as a function of Pla at constant Q in an anesthetized dog before (stippled line) and after (full line) injection of oleic acid (OA) to produce an acute lung injury. Lung injury was associated with a shift of linear Ppa-Q relationships to higher pressures, with increased extrapolated pressure intercept (small stipple line). Pla was transmitted to Ppa in a close to 1/1 relationship before oleic acid, but only at a pressure equal to the extrapolated pressure intercept of Ppa-Q after oleic acid, which is compatible with an increased closing pressure becoming the effective downstream pressure of the pulmonary circulation. From reference 121.