Fig. 3.
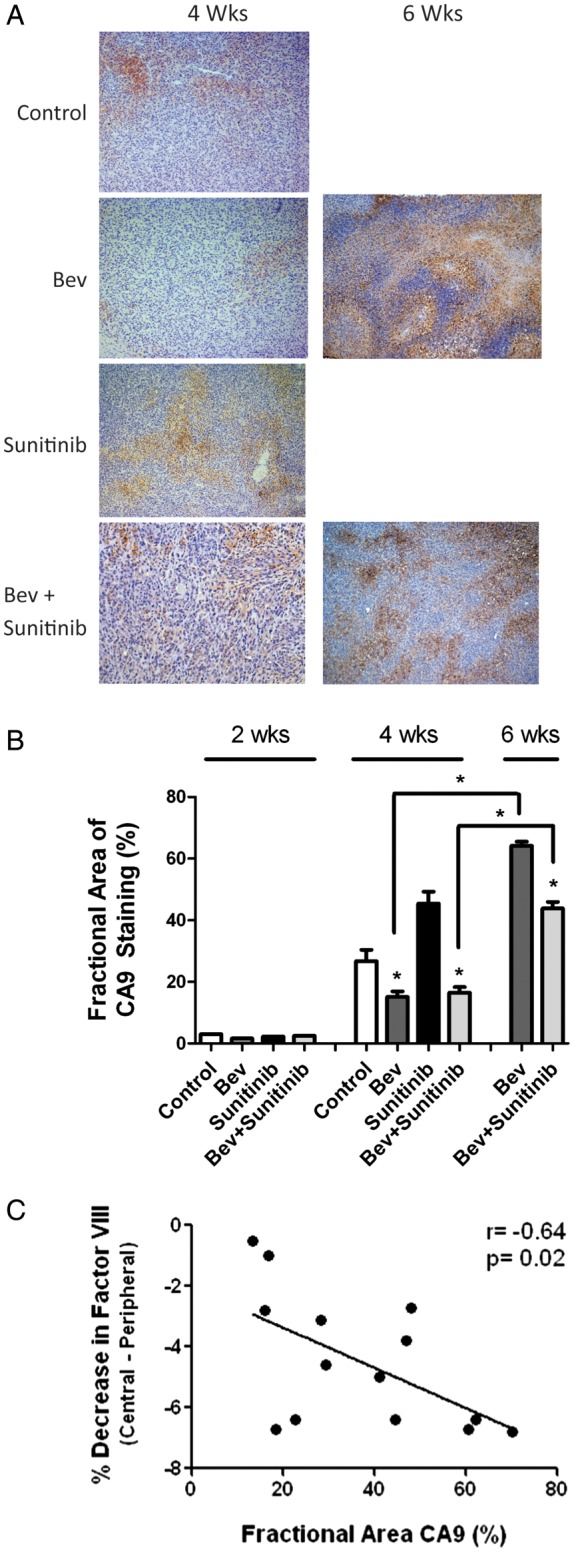
VEGFR inhibition induces greater tumor hypoxia than anti-VEGF therapy (A) Representative light microscopy image at 200× magnification showing immunohistochemical detection of carbonic anhydrase 9 (CA9; brown nuclear staining) demonstrating regions of tumor hypoxia in the 4 treatment groups at 4 and 6 weeks. (B) Bar graph depicting the quantification of fractional staining of CA9. *P < .05 compared with controls. (C) An inverse correlation between factor VIII staining and fractional area of CA9 staining was seen for all tumor treatment groups.
