Fig. 1.
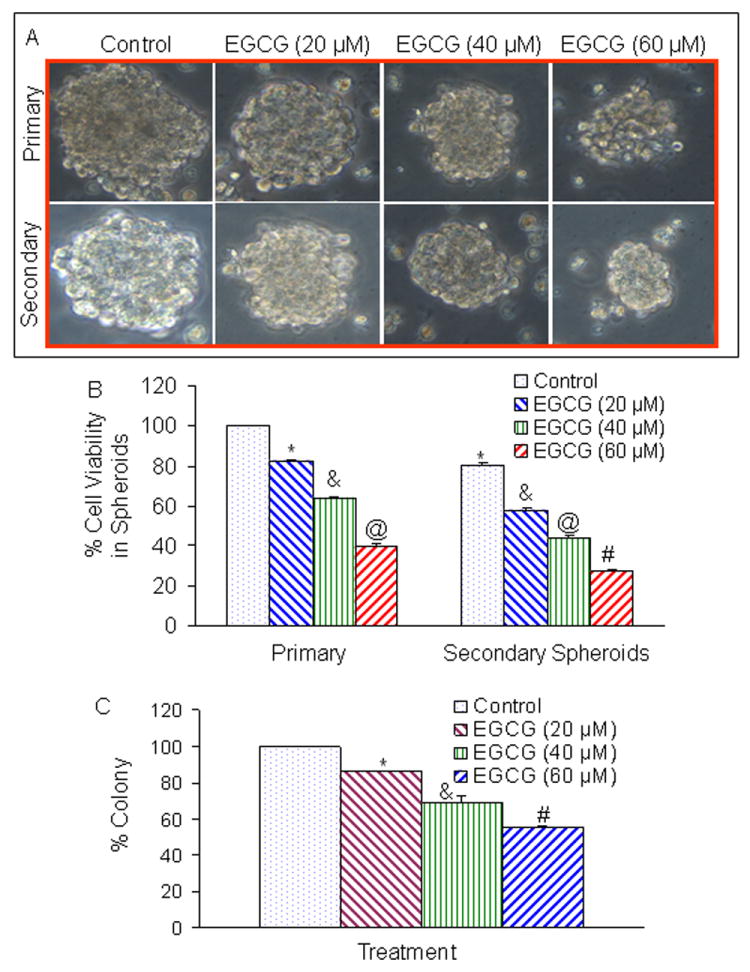
Effects of EGCG on tumor spheroids and cell viability of pancreatic cancer stem cells (CSCs). (A), Pancreatic CSCs were seeded in suspension and treated with EGCG (0-60 μM) for 7 days. Pictures of spheroids formed in suspension were taken by a microscope. (B), Pancreatic CSCs were seeded in suspension and treated with EGCG (0-60 μM) for 7 days. At the end of incubation period, sheroids were collected, and dissociated with Accutase (Innovative Cell Technologies, Inc.). For secondary spheroids, cells were reseeded and treated with EGCG (0-60 μM) for 7 days. Cell viability was measured by trypan blue assay. Data represent mean ± SD. *, &, @, or # = significantly different from respective controls, P < 0.05. (C), EGCG inhibits colony formation by CSCs. Pancreatic CSCs were seeded in soft agar and treated with various doses of EGCG and incubated at 4°C for 21 days. At the end of incubation period, colonies were counted. Data represent mean ± SD. *, & or # = significantly different from respective controls, P < 0.05.
