Fig. 4.
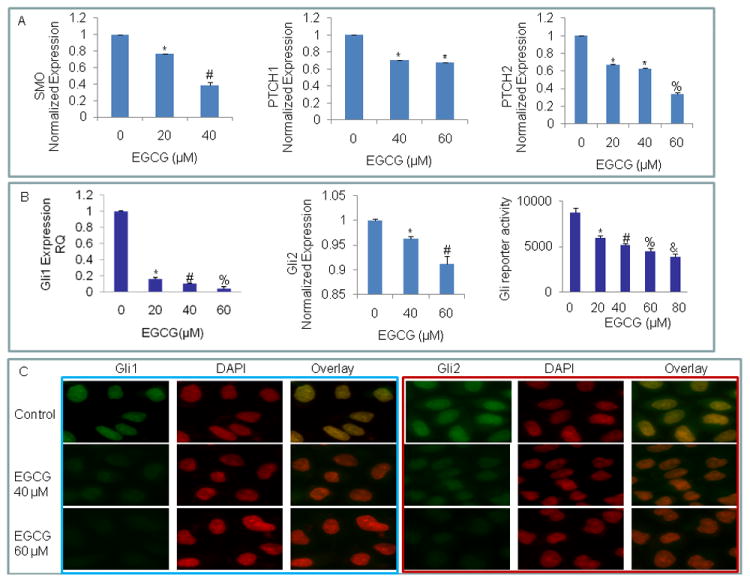
Inhibition of components of sonic hedgehog pathway, Gli transcription and nuclear translocation by EGCG. (A) Inhibition of components of sonic hedgehog pathway and Gli transcription. Pancreatic CSCs were treated with EGCG (0-60 μM) for 36 h. The expression of Smothened (Smo), patched 1 (PTCH1), patched 2 (PTCH2), was measured by q-RT-PCR. Data represent mean ± SD. *, #, or % = significantly different from respective controls, P < 0.05. (B), Inhibition of Gli1 and Gli2 expression and Gli transcription. Pancreatic CSCs were treated with EGCG (0-60 μM) for 36 h. The expression of Gli1 and Gli2 was measured by q-RT-PCR. Gli reporter activity. CSCs were transduced with Gli-responsive GFP/firefly luciferase viral particles (pGreen Fire1-Gli with EF1, System Biosciences). After transduction, culture medium was replaced and CSCs were treated with EGCG (0-60 μM) for 24 h. Gli-responsive reporter activity was measured by luciferase assay (Promega Corporation). Data represent mean ± SD. *, #, % or & = significantly different from respective controls, P < 0.05. (C), EGCG inhibits nuclear translocation of Gli1 and Gli2. Pancreatic CSCs were treated with or without EGCG (40 or 60 μM) for 24 h. At the end of incubation period, CSCs were fixed with paraformaldehyde, permeabilized with titron X100, and blocked with 5% normal goat serum. Cells were then treated with either anti-Gli1 or anti-Gli2 antibody, followed by secondary antibody plus DAPI. Stained cells were mounted and visualized under a fluorescence microscope. Blue fluorescence of DAPI was changed to red color for a better contrast.
