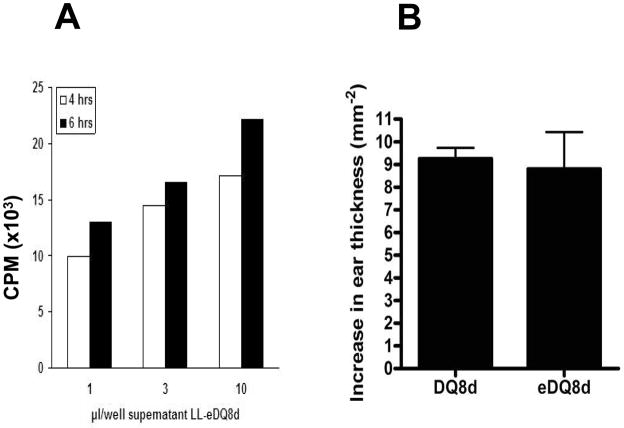
FIGURE 2.
L. lactis -derived eDQ8d exhibits bioactivity as it induces proliferation of human HLA DQ8 T cell clones with no e-tag interference. (A) Human DQ8 T cells were derived as described in the material and methods. LL-eDQ8d was grown overnight and diluted 1:50, 4 and 6 hours thereafter supernatant was collected. Cells were stimulated with 1, 3 or 10 μl supernatant of a LL-eDQ8d culture. (B) For detection purposes an e-tag was attached. To exclude any possible interference of the e-tag, NOD AB° DQ8 transgenic mice were immunized by subcutaneous injection of 100 μg DQ8d with or without e-tag in CFA at day 1. At day 7, mice baseline ear-thickness was measured and mice were challenged with 10 μg DQ8d with or without e-tag, corresponding to the peptide used for the immunization, in 10 μl saline in the auricle of the ear. DTH responses were expressed as the difference in ear-thickness 24 h after the peptide injection minus the ear-thickness before injection. Data represent mean (± SEM) increase in ear thickness of 1 experiment including 6 mice per group.