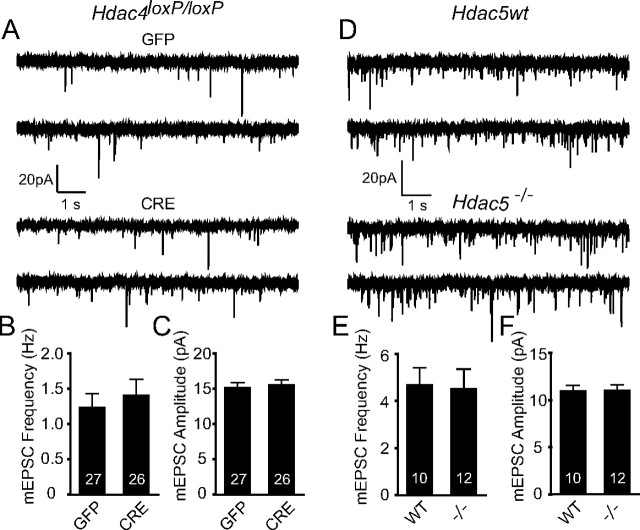
Figure 5.
Deletion of Hdac4 or Hdac5 in hippocampal neurons in culture does not perturb basal synaptic transmission. A, Representative recordings of miniature excitatory events recorded in 1 μm tetrodotoxin and 50 μm picrotoxin from homozygous Hdac4loxP/loxP neurons infected with either high-titer lentivirus expressing GFP and CRE-GFP. B, C, Bar graph depicts that mEPSC frequency and amplitudes remain unchanged upon Hdac4 knockdown. The numbers on the bars indicate the number of experiments. D, Representative recordings of miniature excitatory events recorded from Hdac5−/− and Hdac5wt neurons. E, F, Bar graphs reveal no changes in mEPSC frequency or amplitudes upon Hdac5 deletion. All the recordings were made on 14–17 DIV hippocampal neuronal cultures. Error bars indicate ±SEM.