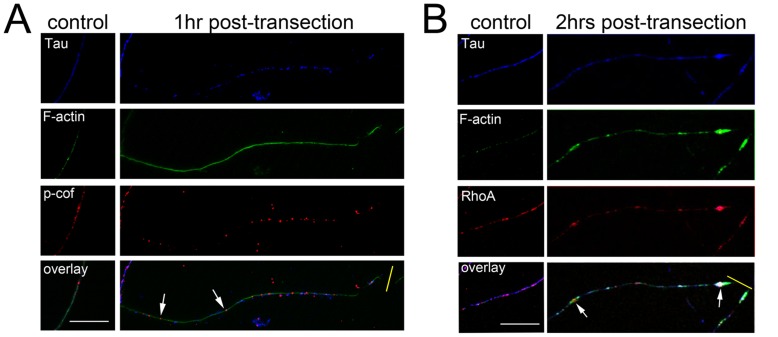
Figure 4. RhoA, phosphorylated cofilin and filamentous actin (F-actin) are modulated in injured axons in vitro.
Primary hippocampal neurons (14DIV) were cultured according to the method of Fath et al (2009) and stained for Tau, RhoA, p-cofilin, and F-actin at 1–2 hrs following transection of their neurites. Uninjured axons revealed amorphous puncta for RhoA, p-cofilin and F-actin that were distributed stochastically with a variable degree of co-localisation (A&B control panels). One hour following transection (yellow bar) F-actin staining appeared smooth and more intense with a concomitant redistribution of p-cofilin into widely-spaced circular puncta as indicated with arrows (A). After 2 hrs following transection, RhoA was observed to be concentrated in F-actin rich structures (B); in particular, large RhoA-positive swellings were observed (arrows), which also occasionally presented as enriched in tau (B). Scale bar = 10 µM.