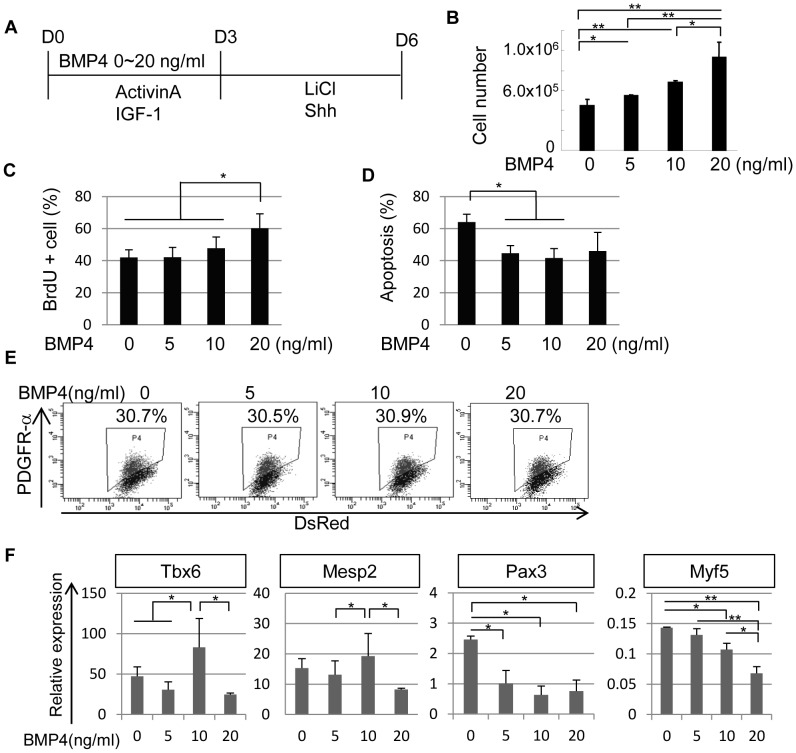
Figure 2. Effects of BMP4 on paraxial mesodermal differentiation of mouse iPS cells.
(A) A scheme for the paraxial mesodermal differentiation of mouse iPS cells with different concentrations of BMP4 from D0 to D3. BMP4 was administrated from D0 to D3 at a concentration of 0–20 ng/ml. The cultures also contained Activin A (5 ng/ml), IGF-1 (10 ng/ml), LiCl (5 mM), and Shh (10 ng/ml). The cells were analyzed on D6 in (B), (E), and (F), or on day 3 (D3), as shown in (C) and (D). (B) Total number of mouse iPS cells after differentiation with the protocol shown in (A) (n = 3). (C) Proliferation of differentiated mouse iPS cells on D3 assessed by BrdU assay (n = 3). (D) Apoptosis of differentiated mouse iPS cells on D3 assessed by a proportion of PI positive/AnnexinV positive cell (n = 3). (E) The expression of PDGFR-α in mouse iPS cell differentiation culture. The percentage indicates the proportion of PDGFR-α+ cells (n = 3), which was not affected by BMP4. (F) Gene expression profiles of PDGFR-α+ cells in BMP4-induced cultures (n = 3). The expression of Tbx6 and Mesp2 was higher at a concentration of 10 ng/ml BMP4, whereas the expression of Pax3 and Myf5 was reduced at higher doses of BMP4. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 between selected two samples.