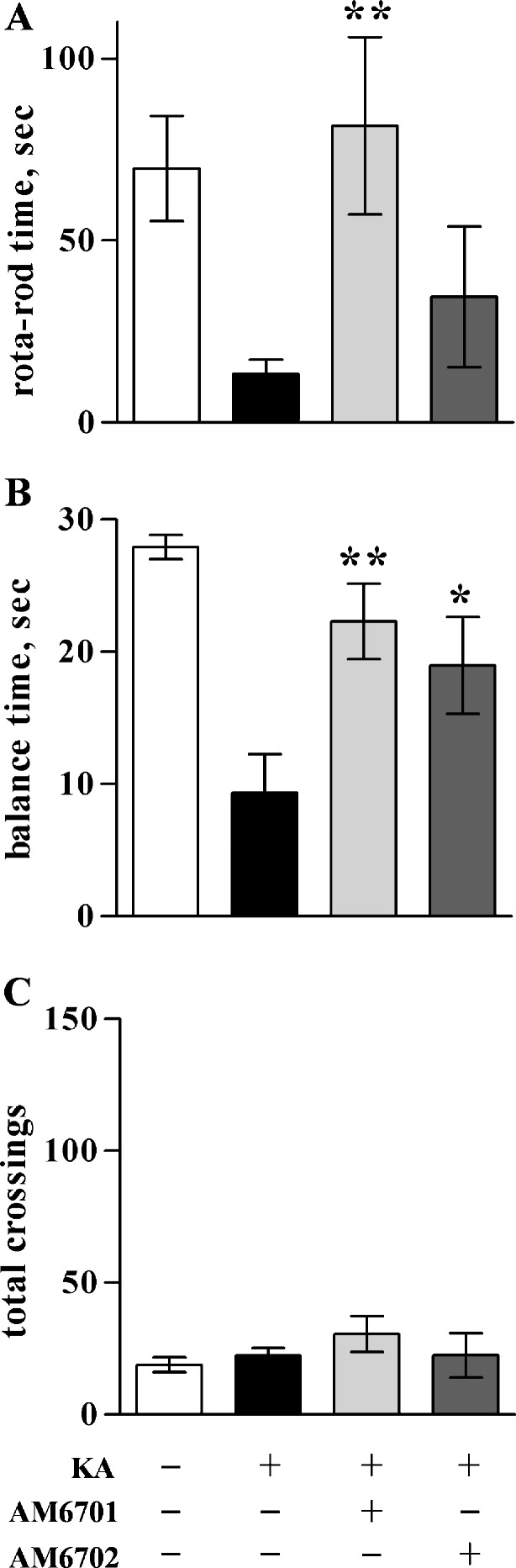
Fig. 6.
Improved balance and coordination in the KA rat model. Seizures were initiated by KA injections (9.8 mg/kg), followed by immediate injections of vehicle (n = 10–16) or 5 mg/kg AM6701 or AM6702 (n = 6–8). No-insult control rats received 2 vehicle injections (n = 12–13). At 24-h post-injection, the animals were evaluated with a rotarod paradigm to assess their coordination, as determined by the mean time ± SEM maintaining coordinated movement on a rod rotating at 15 rpm (a). At 48-h post-injection, the different treatment groups were assessed for their balance time (mean ± SEM) when placed on a narrow, suspended bar (b). The rats were also monitored for locomotor activity in a novel open field, determining mean number ± SEM of area segments crossed into during the exploring period (c). Analysis of variance, p < 0.01 (a), p < 0.0001 (b); post hoc tests compared to KA only group: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01