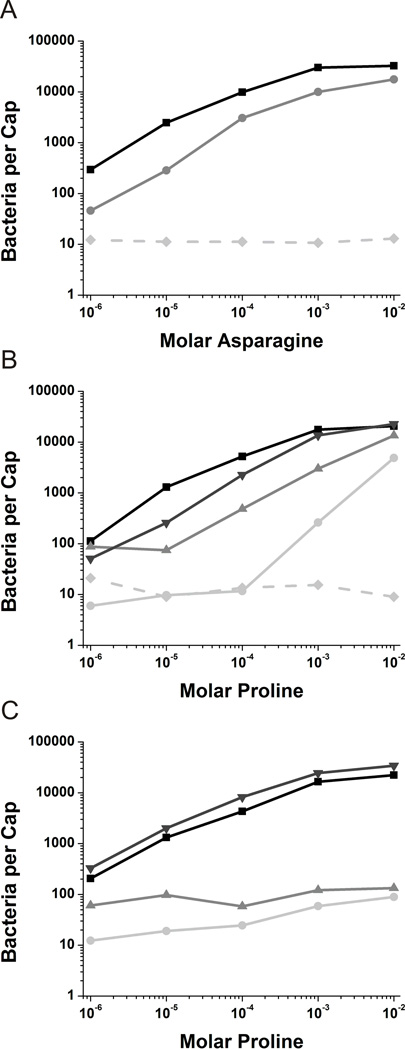
Fig. 1.
Capillary assays in cheD genetic backgrounds.
A. Capillary assays towards asparagine with mcpB expressed in the Δ10mcp background (■) and the Δ10mcp cheD background ( ). The Δ10mcp strain (
). The Δ10mcp strain ( ) is included as a negative control.
) is included as a negative control.
B. Capillary assays towards proline with mcpC expressed in the Δ10mcp background (■), mcpC expressed in the Δ10mcp cheD background ( ), mcpC-Q609E expressed in the Δ10mcp background (▼) and mcpC-Q609E expressed in the Δ10mcp cheD background (
), mcpC-Q609E expressed in the Δ10mcp background (▼) and mcpC-Q609E expressed in the Δ10mcp cheD background ( ). The Δ10mcp strain (
). The Δ10mcp strain ( ) is included as a negative control.
) is included as a negative control.
C. Capillary assays towards proline with all other nine chemoreceptors present. Wild-type strain OI1085 (■), mcpC expressed in the cheD mcpC knockout ( ), mcpC-Q609E expressed in the mcpC knockout (▼) and mcpC-Q609E expressed in the cheD mcpC knockout (
), mcpC-Q609E expressed in the mcpC knockout (▼) and mcpC-Q609E expressed in the cheD mcpC knockout ( ).
).