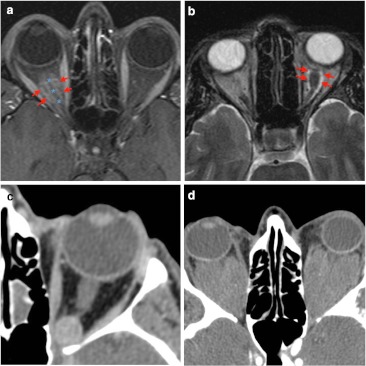
Fig. 7.
Examples of intra-conal mass-like lesions are given. a Fat-suppressed T1-weighted imaging shows tubular mass lesion which enhances intensively after contrast. On this axial image, the optic nerve (blue asterisk) appears as a negative defect in relation to the surrounding optic nerve sheath meningioma (red arrows), producing “the tram track sign”. b Optic glioma (red arrows) presents intra-conal mass and high signal intensity on axial T2-weighted imaging. This glioma is seen as a fusiform and well-defined lesion without intracranial extension. The patient presented a clinical history of vision loss. c Contrast CT scan presents an intra-conal well-defined round lesion. On venous phase CT shows homogeneous delayed enhancement in keeping with cavernous hemangioma. d Non-contrast CT scan shows bilateral homogeneous lesions in patient diagnosed of Erdheim-Chester disease. Typical location is intra-conal, so there is marked displacement of conal muscle due to the large size of the lesion