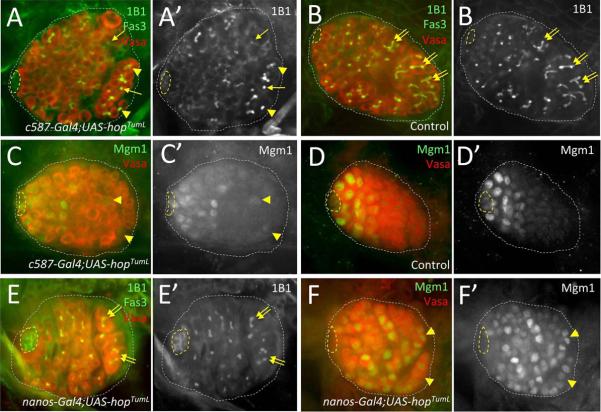
Figure 5. Impact of germline vs. somatic Jak-STAT activation on GSC maintenance and gene expression.
Late- 1st instar and early 2nd instar larval testes immunostained with anti-Vasa (A–F, red; A”–F” alone), and either anti-1B1 E' alone) to reveal fusomes, or anti-(β-galactosidase (C, D, & F, green; C', D' & F' alone) to reveal expression of the enhancer trap Mgml. All images with testis anterior oriented left. Hub (yellow dashed lines) and testes (white dotted lines) outlined. [A, B] Early-L2 testis with Jak hyper-activated in somatic cells (A; c587-Gal4/+;UAS-hopTumL/+) showing germ cells with rounded fusomes (yellow arrows) and aberrant branching (yellow arrowheads) in the testis posterior, whereas elongation and branching of fusomes (yellow double-arrows) is observed in posterior germ cells of an age-matched sibling control (B; c587-Gal4/+; CyO/+). [C, D] Late-Ll testis after somatic Jak hyper-activation (C; c587-Gal4/+; Mgm1/UAS-hopTumL) showing Mgm1 expression in a small subset of germ cells at the testes posterior (yellow arrowheads), while Mgml expression is restricted to GSCs and early gonialblasts in an age-matched sibling control (D; c587-Gal4/+; Mgm1/+). [E, F] Early-L1 testis with Jak hyper-activated specifically in the germline (E, F; UAS-hopTumL/Mgml; nanos-Gal4/+) showing (E) normal germ cell differentiation with spherical fusomes in GSCs and gonialblasts adjacent to the hub, and branched fusomes (yellow double-arrows) in distally-localized spermatogonia, as well as (F) expression of Mgml in germ cells throughout the testis, including differentiating spermatogonia at the testis posterior (yellow arrowheads).