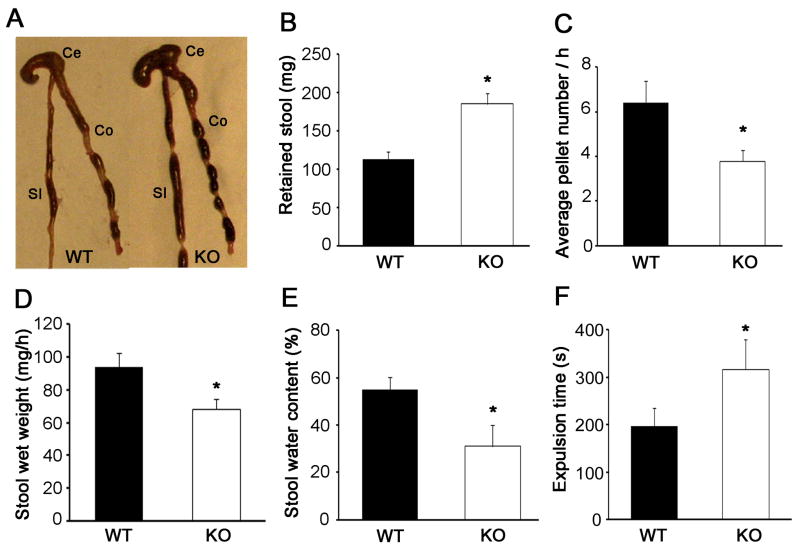
Figure 2. Stool retention and colonic transit in HB-EGF KO and WT mice.
(A) Representative photograph showing increased stool retention in HB-EGF KO mouse colon; (B) weight of retained colonic contents in WT and HB-EGF KO mice. n=6 animals/group; (C) average number of stool pellets passed per hour in WT and HB-EGF KO mice. n=5 animals/group; (D) stool wet weight in WT and HB-EGF KO mice. n=5 animals/group; (E) stool water content in WT and HB-EGF KO mice. n=5 animals/group; and (F) glass bead expulsion time. n=8 animals/group. All data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. SI: small intestine; Ce: cecum; Co: colon.