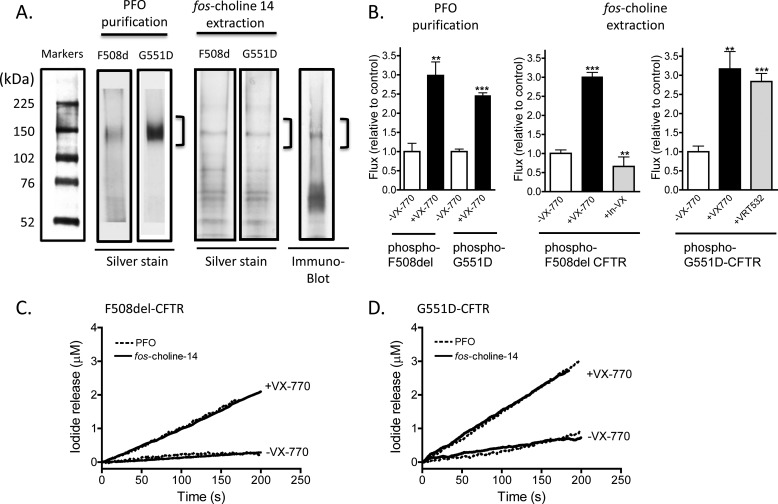
FIGURE 5.
VX-770 acts directly to potentiate phosphorylated F508del-CFTR and phosphorylated G551D-CFTR in the absence of Mg-ATP. A, SDS-PAGE analysis and silver stain of purified F508del-CFTR and purified G551D-CFTR protein isolated using the PFO detergent extraction method. In this method, the mutant CFTR proteins are solubilized in PFO and applied to a Ni-NTA affinity column. The full-length mutant protein is eluted by the application of a continuous pH gradient (FPLC). The PFO method requires 3 days and yields functional protein as published previously (12, 18–23, 47–49). The full-length PFO-purified proteins run as expected as broad 150-kDa bands in overloaded gels as expected for Sf9-expressed proteins (21). Data are representative of 10 separate purifications. However, full-length (150 kDa) mutant proteins plus other proteins are evident in silver-stained gels after the fos-choline 14-based methods (a method wherein CFTR protein solubilized in fos-choline is eluted from a Ni-NTA affinity column in a batchwise method described for the first time in this paper and requiring half a day). Immunoblots using a CFTR-selective antibody shows that other bands likely correspond to CFTR fragments. Hence, the fast batchwise method employing fos-choline purifies the full-length mutants plus degradation products. Data are representative of three separate purifications. B, initial iodide efflux rates mediated by phosphorylated F508del-CFTR or phosphorylated G551D-CFTR are potentiated by VX-770 (10 μm) in the presence of 1 mm ATP, regardless of the purification method used (PFO or fos-choline). These data show that the activity mediated by reconstituted fos-choline-extracted and Ni-NTA-purified mutant CFTR is conferred by the full-length mutant protein. An inactive analog of VX-770 (V-09-1188, labeled In-VX, provided by Vertex Pharmaceuticals) fails to mediate potentiation of F508del-CFTR, whereas P1 (or VRT-532) is effective in potentiating G551D-CFTR. Means ± S.E. of five and four studies for the PFO purification and three and five studies for the fos-choline method for F508del-CFTR and G551D-CFTR, respectively, are shown. **, p = 0.0034 for PFO-purified F508del-CFTR in the presence versus absence of VX-770; p = 0.001 for fos-choline purified F508del-CFTR in the presence of In-VX versus sample treated with VX-770; and p = 0.0019 for fos-choline purified G551D in the presence of VX-770 versus its absence. ***, p ≤ 0.0001, when compared with the associated control sample in the absence of VX-770. PKA-phosphorylated F508del-CFTR (C) or PKA phosphorylated G551D-CFTR (D) purified using either method exhibits potentiation by VX-770 in the nominal absence of Mg-ATP. We show traces representative (n = 3) for mutant proteins extracted either using fos-choline 14 or PFO detergent (B and C). Samples were phosphorylated with 200 nm and 1 mm ATP and treated with 10 μm VX-770, In-VX, or VRT-532 where indicated. The similarity of these responses support the idea that the activities shown for fos-choline-extracted mutant proteins report the intrinsic activities of the full-length mutants and support the utility of this rapid process for studying mutant CFTR proteins in a cell-free reconstitution system that enables excellent control of ligand concentrations.