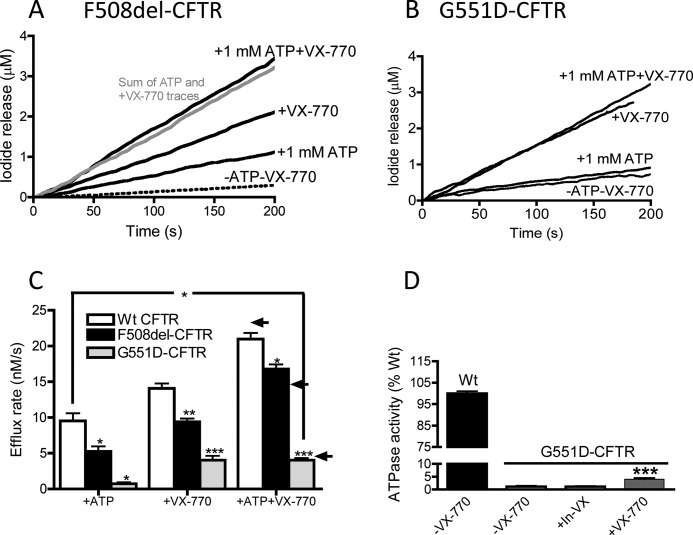
FIGURE 6.
Additive effect of VX-770 and ATP in regulation of phosphorylated F508del-CFTR and phosphorylated G551D-CFTR. Representative iodide efflux traces are from proteoliposomes containing F508del-CFTR (A) or G551D-CFTR (B). Additive effect of ATP (1 mm) and VX-770 (10 μm) on F508del-CFTR. In contrast to F508del-CFTR (and WT-CFTR), G551D-CFTR proteoliposomes are not activated Mg-ATP but do show robust response to VX-770 alone. C, bar graph shows summary data for initial flux rates by the WT-CFTR and mutant CFTR proteins. Data are means of three replicates ± S.E., except for WT +ATP and WT +ATP VX-770, which are means of 10 ± S.E., and the G551D-CFTR data, which are means of 5–7, respectively, ± S.E. Samples were normalized to their respective untreated sample (−ATP-VX-770). Asterisks indicate samples that are significantly different from values for WT-CFTR treated similarly; * 0.05>p > 0.01; ** 0.01>p > 0.001; ***, p < 0.001. Arrows to the right indicate the mathematical addition of VX-770 alone flux and ATP alone flux values for upper WT-, middle F508del-, and lower G551D-CFTR. D, VX-770 modestly increases the ATPase activity of G551D-CFTR. Significantly more ATPase activity was measured for PKA-phosphorylated G551D-CFTR samples treated with VX-770 versus control (***, p < 0.0001) or the inactive analog (In-VX, p = 0.0027). Bars represent the mean of 3 (WT-CFTR), 22 (−VX-770), 17 (+VX-770), or 7 (In-VX) trials ± S.E.