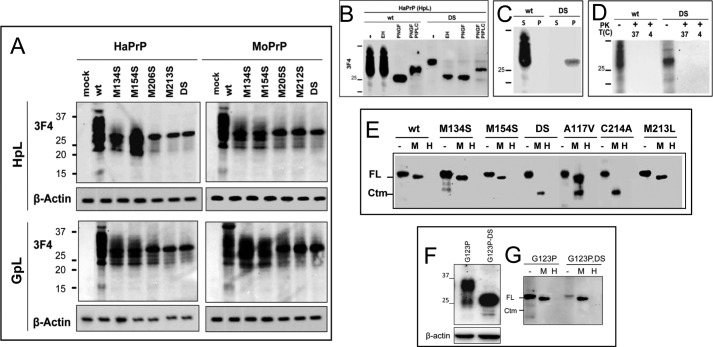
FIGURE 2.
Molecular features of PrP mutants in mammalian cells. A, transient expression of HaPrP and MoPrP WT and mutants in HpL and GpL cells. The signal corresponding to β-actin is displayed at the bottom of each membrane. B, PNGase F, Endo H, and PIPLC digestions of HaPrP WT and HaPrPDS expressed in HpL cells. C, differences in the detergent solubility of HpL-expressed HaPrP WT and HaPrPDS determined by partitioning between the soluble and pellet fraction of an ultracentrifugation. D, protease sensitivity at 37 and 4 °C of HpL-expressed HaPrP WT and HaPrPDS probed by PK digestion. E, PK protection of PrP chains in intact (M) and lysed (H) microsomes isolated from HpL-expressed HaPrP WT, M134S, M154S, DS, C214A, M213L, and A117V, this last taken as positive control for CtmPrP topology. F, transient expression of HaPrPG123P and HaPrPG123PDS in HpL cells. The signal corresponding to β-actin is displayed at the bottom. G, PK protection of PrP chains in intact (M) and lysed (H) microsomes isolated from HpL transiently expressing HaPrPG123P and HaPrPG123PDS mutants. PrP immunoblotting was performed with mAb 3F4.