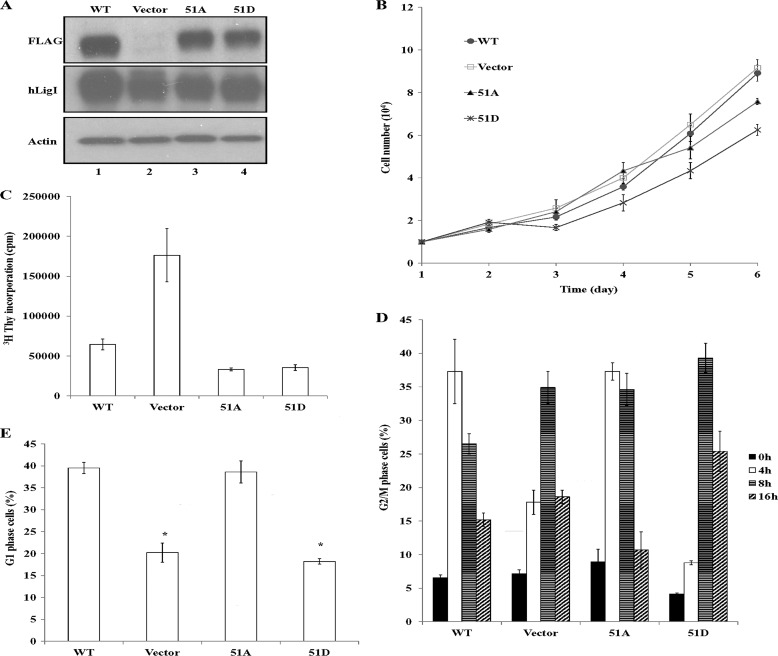
FIGURE 3.
Expression of hLigI51A and hLigI51D in hLigI-deficient cells and effects on proliferation and DNA synthesis. A, extracts (20 μg) from 46BR.1G1 cells that stably express the following: lane 1, FLAG-tagged wild-type hLigI; lane 2, no FLAG-tagged protein; lane 3, FLAG-tagged hLigI51A; lane 4, FLAG-tagged hLigI51D. The levels of endogenous and FLAG-tagged hLigI (LigI and FLAG) and β-actin (Actin) in the extracts were determined by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. B, growth of derivatives of 46BR.1G1 cells either transfected with the empty vector (□) or expressing FLAG-tagged wild-type hLigI (●), hLigI51A (▴) or hLigI51D (cross). The graph shows data compiled from three independent experiments, with the error bars indicating mean ± S.E. C, the indicated 46BR.1G1 derivatives were seeded in duplicate into 60-mm dishes (105 cells/dish). After 3 days, [3H]thymidine was added for 30 min. Incorporation of [3H]thymidine into DNA was measured by liquid scintillation counting. The graphs shows data compiled from two independent experiments, with the error bars indicating mean ± S.E. D and E, the indicated 46BR.1G1 derivatives were synchronized in early S phase as described under “Experimental Procedures” and then harvested at 0, 4, 8, and 12 h after release. The percentage of G2/M cells at each time point (D) and the percentage of G1 cells after 8 h (E) were determined by FACS. The graph shows data compiled from three independent experiments, with the error bars indicating S.D. *, p < 0.001 compared with cells expressing FLAG-tagged wild-type hLigI.