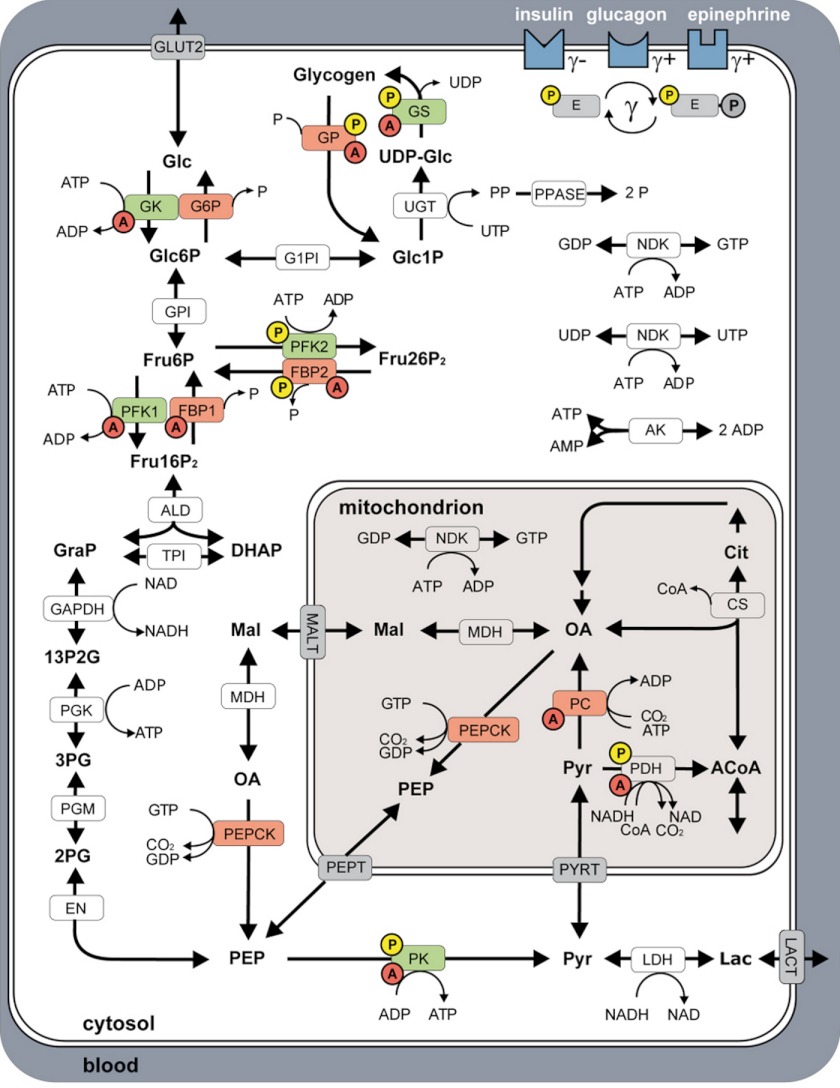
FIGURE 1.
Model of human hepatocyte glucose metabolism comprising glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and the glycogen pathway, and the spatial reaction compartments: blood, cytosol, and mitochondrion. The figure is reproduced from Ref. 18. Key enzymes of HGP are depicted in red, key enzymes of HGU in green. Enzymes regulated via allosteric mechanisms are marked with red A, interconvertible enzymes with yellow P. Insulin, glucagon, and epinephrine regulate the glucose metabolism by changing the phosphorylation state (γ) of key interconvertible enzymes, with insulin (γ) decreasing, epinephrine (γ+) and glucagon (γ+) increasing γ. Reactions: ALD, aldolase; AK, adenylate kinase; CS, citrate synthase; EN, enolase; FBP1, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase; FBP2, fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-phosphate dehydrogenase; G1PI, glucose-1 phosphate-1,6-phosphomutase; G6P, glucose-6-phosphatase; GK, glucokinase; GLUT2, glucose transporter 2; GP, glycogen phosphorylase; GPI, glucose-6-phosphate isomerase; GS, glycogen synthase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MALT, malate transporter; MDH, malate dehydrogenase; NDK, nucleoside diphosphate kinase; PC, pyruvate carboxylase; PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; PEPT, phosphoenolpyruvate transporter; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PFK1, phosphofructokinase 1 PFK2, phosphofructokinase 2; PGK, phosphoglycerate kinase; PGM, 3-phosphoglycerate mutase; PK, pyruvate kinase; PPASE, pyrophosphate phosphohydrolase; PYRT, pyruvate transporter; TPI, triose-phosphate isomerase; UGT, UTP:glucose-1 phosphate uridylyltransferase. Metabolites: 13P2G, 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; 2PG, 2-phosphoglycerate; 3PG, 3-phosphoglycerate; ACoA, acetyl-CoA; Cit, citrate; CoA, coenzyme A; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; Fru16P2, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; Fru26P2, fructose 2,6-bisphosphate; Fru6P, fructose 6-phosphate; Glc, glucose; Glc1P, glucose 1-phosphate; Glc6P, glucose 6-phosphate; GRAP, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; Lac, lactate; OA, oxalacetate; Mal, malate; P, phosphate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PP, pyrophosphate; Pyr, pyruvate; UDP-Glc, UDP-glucose. For detailed description see ”Materials and Methods“ and Ref. 18.