FIGURE 5.
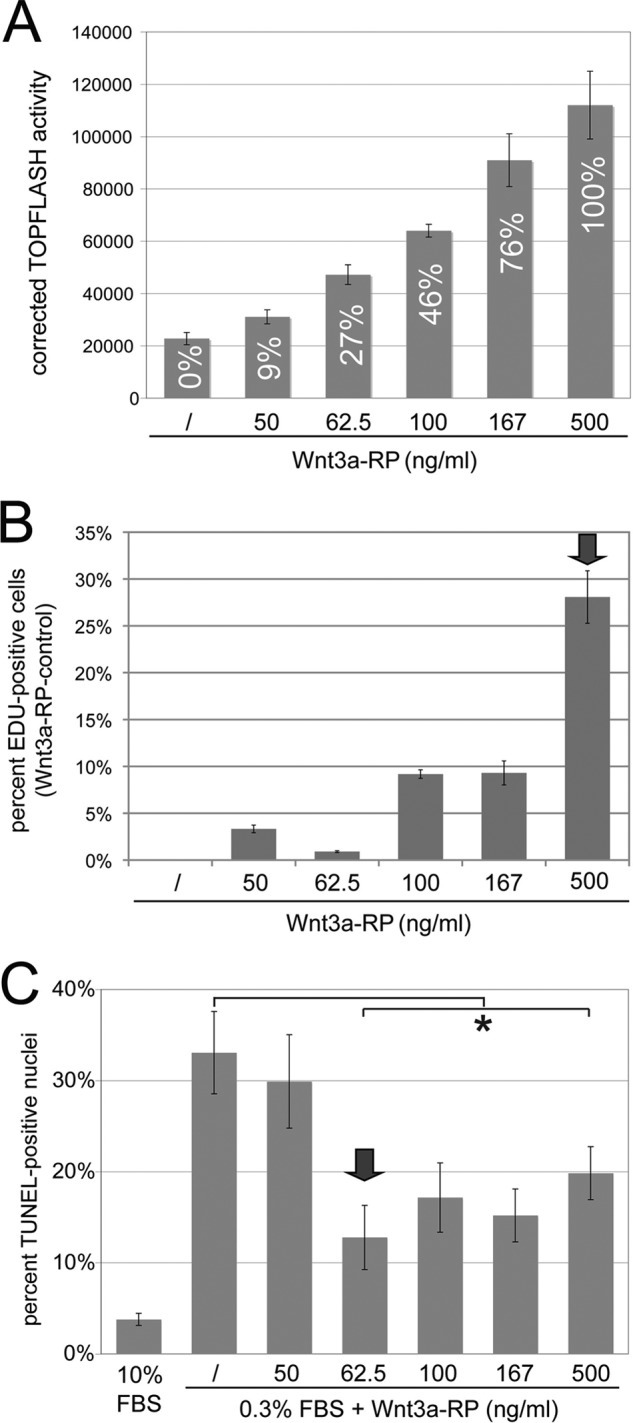
Differential Wnt3a thresholds control proliferation versus apoptosis. A, establishment of a TOPFLASH Wnt3a signaling gradient with Wnt3a-RP. Wnt3a-RP at 0, 50, 62.5, 100, 167 and 500 ng/ml resulted in TOPFLASH activities (Wnt3a-RP/control) of 0, 9, 27, 46, 76, and 100%, respectively. The concentration of 500 ng/ml is above the concentrations frequently used for Wnt3a-RP, and TOPFLASH activity at this concentration was set arbitrarily to 100%. B, quantification of EdU incorporation to measure proliferation of NIH3T3 cells. Cells were treated with Wnt3a-RP for 24 h at 0% (/), 9% (50 ng/ml Wnt3a-RP), 27% (62.5 ng/ml Wnt3a-RP), 46% (100 ng/ml Wnt3a-RP), 76% (167 ng/ml Wnt3a-RP), or 100% (500 ng/ml Wnt3a-RP). The percentage of EdU-positive nuclei in relation to total DAPI-stained nuclei was established for all conditions; subsequently, the value for control conditions (/) was set to zero and subtracted from experimental condition to show the percent increase in EdU-positive cells obtained with Wnt3a treatment over control conditions. Wnt3a signaling levels of 9% (50 ng/ml Wnt3a-RP), 27% (62.5 ng/ml Wnt3a-Rp), 46% (100 ng/ml Wnt3a-RP), and 76% (167 ng/ml Wnt3a-RP) increased EdU incorporation by 1–10% when compared with unstimulated cells (/). At 100% signaling activity (500 ng/ml Wnt3a-RP), a dramatic increase of EdU-positive cells to 28% was observed. The arrow marks the signaling level with maximum biological response. C, quantification of serum starvation-induced apoptosis by TUNEL assay in the presence of Wnt3a-RP gradient signaling levels. Cells were treated in medium containing 0.3% serum and with the indicated concentrations of Wnt3a-RP for 24 h. The percentage of TUNEL-positive cells was quantified by co-staining with DAPI. Control cells in 10% serum showed ∼3% TUNEL-positive cells; this increased to 33% when cell were incubated in 0.3% serum. Low Wnt3a signaling activity of 9% (50 ng/ml Wnt3a-RP) was not able to significantly interfere with apoptosis. However, a Wnt3a signaling activity of 27% (62.5 ng/ml Wnt3a-RP) was able to significantly reduce apoptosis to 13% (*, p < 0.05). Higher Wnt3a signaling activities of 46, 76, or 100% reduced TUNEL staining to a degree similar to that seen with 27% Wnt3a activity. The arrow marks the lowest signaling level with maximum biological response.
