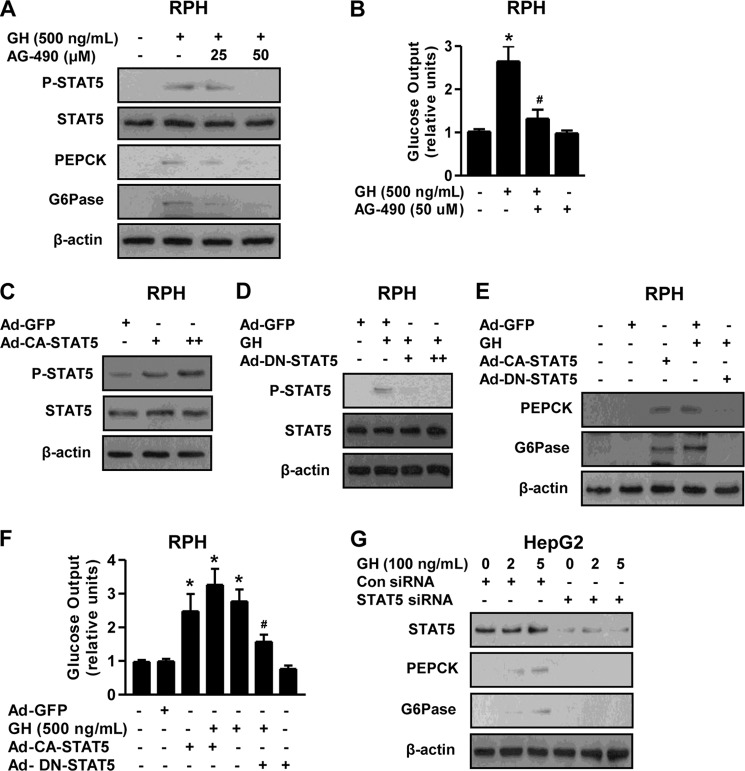
FIGURE 2.
STAT5 mediates GH-mediated induction of hepatic gluconeogenesis. A, RPHs were pretreated with AG490 for 6 h and then exposed to GH (500 ng/ml) for 3 h at the various concentrations. Whole cell extracts were isolated and analyzed using Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. Protein levels were normalized to β-actin level and/or total form. B, glucose output assay in RPHs was performed with GH and AG490 at the indicated concentrations in glucose-free medium supplemented with gluconeogenic substrate sodium lactate (20 mm) and sodium pyruvate (1 mm). C, RPHs were infected with Ad-GFP and Ad-CA-STAT5 for 36 h. D, RPHs were infected with Ad-DN-STAT5 for 36 h and then treated with GH for 3 h. Whole cell extracts were isolated and analyzed using Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. E, RPHs were infected with Ad-GFP, Ad-CA-STAT5, and Ad-DN-STAT5 for 36 h and then treated with or without GH for 3 h. Whole cell extracts were isolated and analyzed using Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. F, glucose output assay in RPH was conducted as described for B, using glucose-free medium supplemented with the gluconeogenic substrate sodium lactate (20 mm) and sodium pyruvate (1 mm). All of the data are representative of at least three independent experiments. G, HepG2 cell lines were transfected with siRNA control and siRNA STAT5 for 36 h and then treated with or without GH for 3 h. Whole cell extracts were isolated and analyzed using Western blot analysis with various antibodies. Protein levels were normalized to β-actin level and/or total forms. *, p < 0.05 (Student's t test); #, p < 0.05 compared with untreated control and/or GH-treated cells (Student's t test or ANOVA).