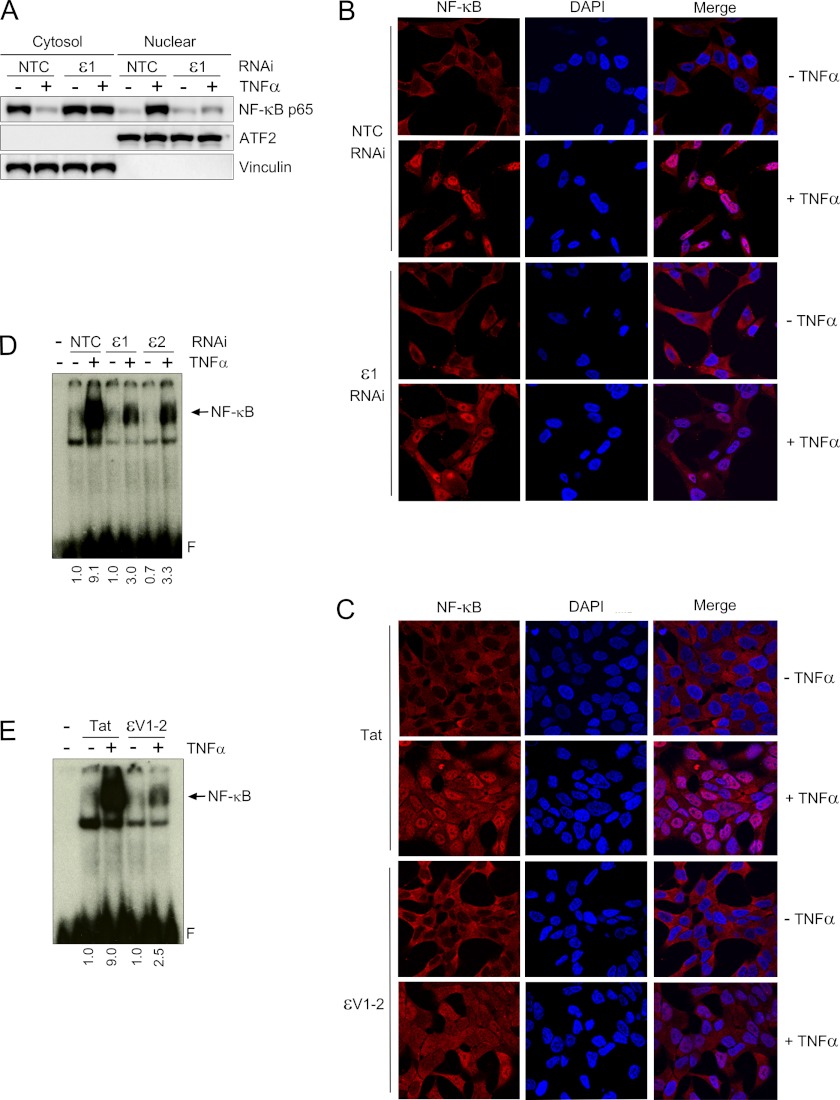
FIGURE 3.
PKCϵ mediates TNFα-induced NF-κB activation in LNCaP cells. A, LNCaP cells were transfected with either PKCϵ (ϵ1) or non-target control (NTC) RNAi duplexes and, 48 h later, stimulated with either TNFα (10 ng/ml) or vehicle for 30 min. Western blot analysis for p65 NF-κB was carried out in cytosolic and nuclear fractions using vinculin and ATF2 as loading controls for each fraction. B, nuclear translocation of NF-κB was assessed by immunocytochemistry in LNCaP cells treated with either TNFα (10 ng/ml) or vehicle for 30 min. Experiments were carried out 48 h after transfection with either ϵ1 or NTC RNAi duplexes. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Cells were visualized by confocal microscopy. Similar results were obtained in at least three independent experiments. C, similar experiments as those in B were carried out in LNCaP cells treated with either ϵV1–2 or Tat peptides (1 μm). D, NF-κB-DNA binding was assessed by EMSA in nuclear extracts prepared 30 min after TNFα or vehicle treatment. Experiments were carried out 48 h after transfection with either ϵ1 or NTC RNAi duplexes. Relative optical density is indicated underneath each lane. E, similar experiments as those in D were carried out in LNCaP cells treated with either ϵV1–2 or Tat peptides (1 μm, 1 h). In all cases, similar results were obtained in at least three independent experiments. Relative optical density is indicated underneath each lane.