Abstract
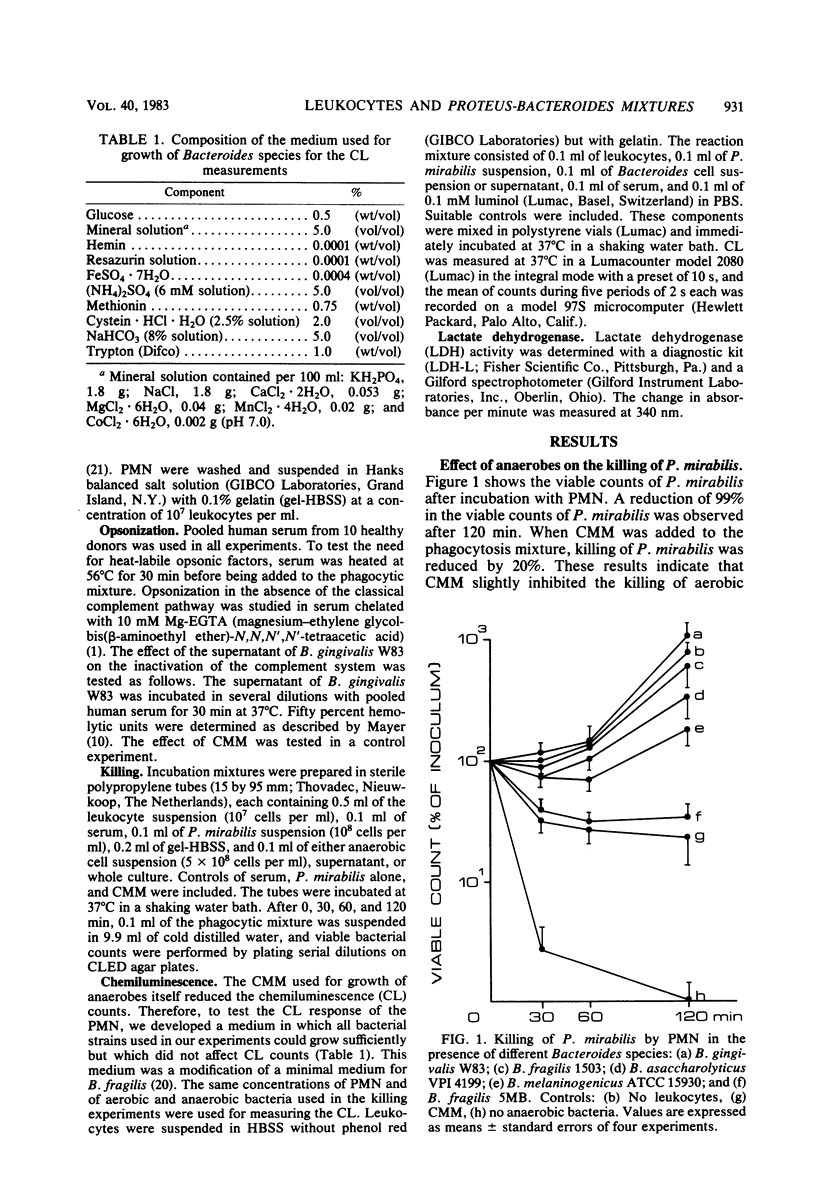
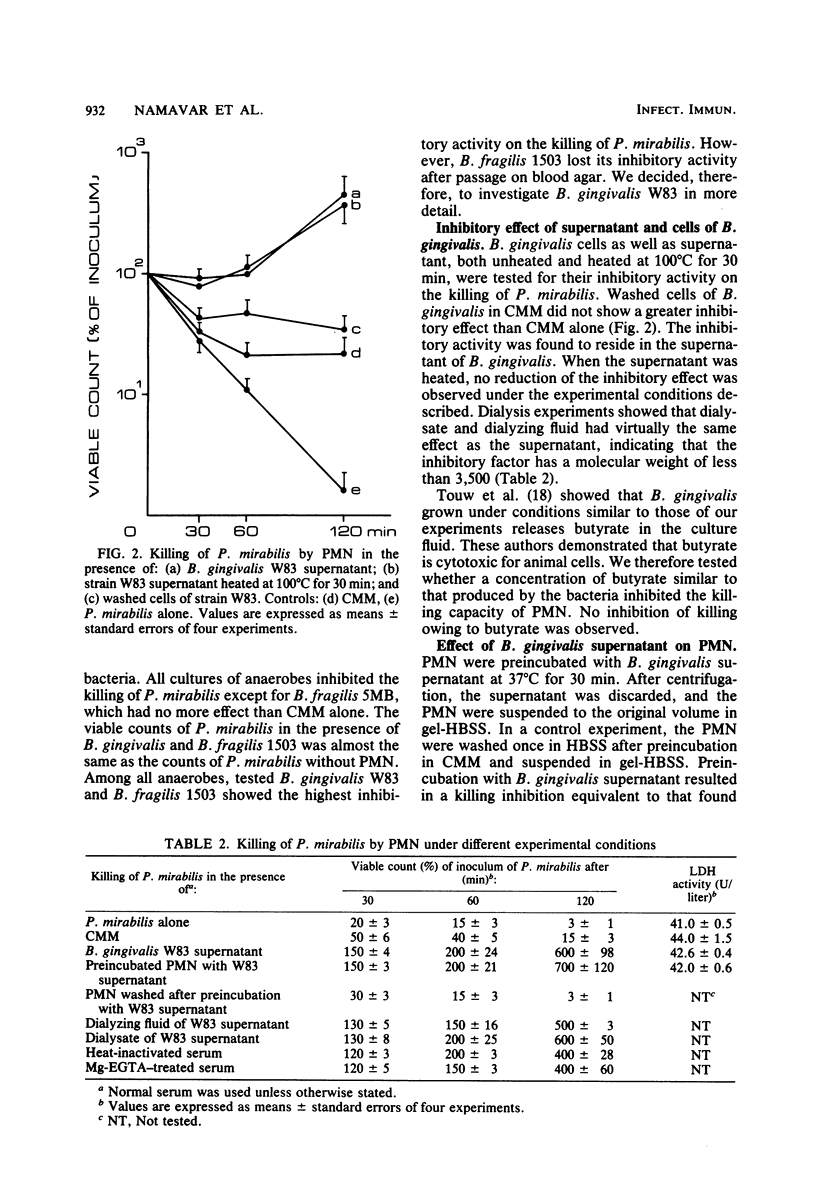
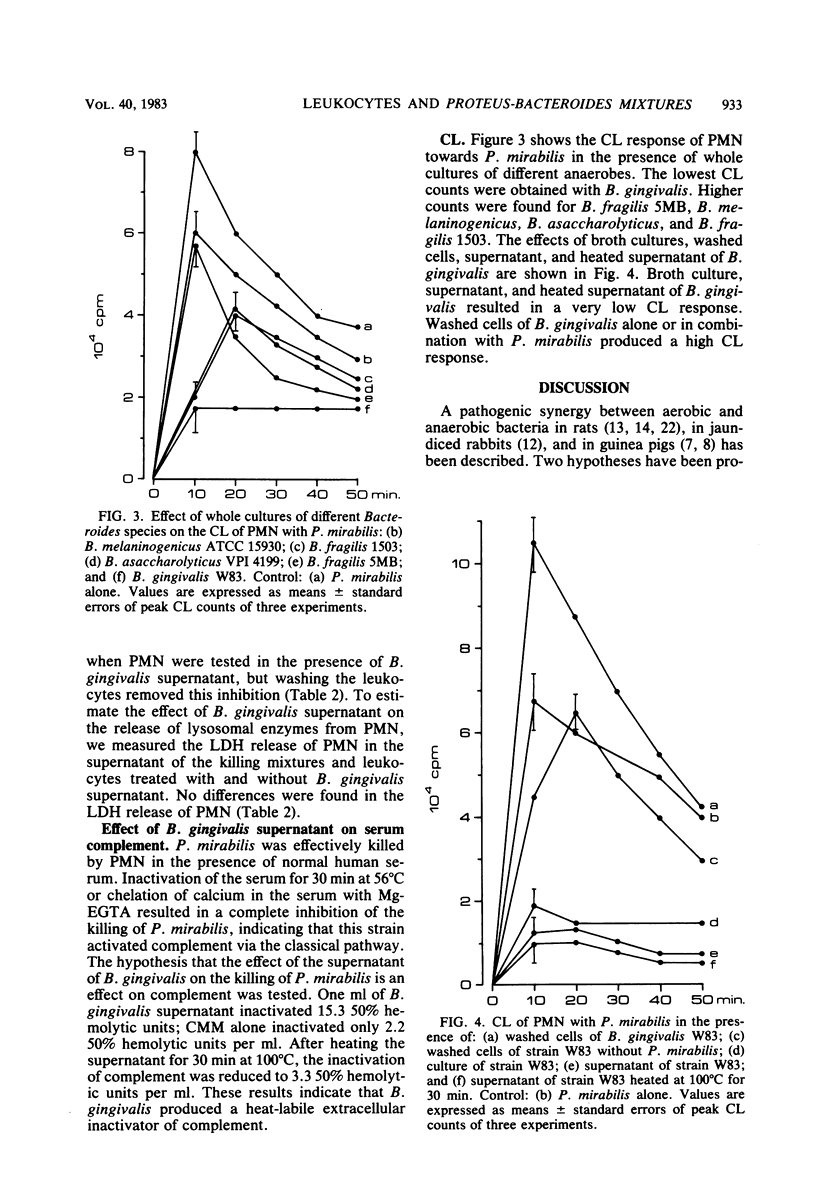
Killing of Proteus mirabilis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes was tested in the presence of different Bacteroides species. In vitro experiments showed that anaerobic bacteria interfered with the killing of aerobic bacteria. However, this inhibitory effect was not a property of all Bacteroides species. Bacteroides gingivalis W83 showed the greatest inhibitory effect of the five Bacteroides strains tested. Killing of P. mirabilis was inhibited by the culture supernatant of B. gingivalis but not by washed cells. Two factors were found in the supernatant of B. gingivalis to account for the inhibitory effect. One was heat stable with a molecular weight of less than 3,500 and inhibited the killing activity of leukocytes, and the other was heat labile and partly inactivated the complement system. The killing experiments paralleled chemiluminescence measurements.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Forsgren A., Quie P. G. Opsonic activity in human serum chelated with ethylene glycoltetra-acetic acid. Immunology. 1974 Jun;26(6):1251–1256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Bartlett J. G. Anaerobic infections. 1. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 23;290(21):1177–1184. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405232902106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham H. R., Sisson P. R., Tharagonnet D., Selkon J. B., Codd A. A. Inhibition of phagocytosis in vitro by obligate anaerobes. Lancet. 1977 Dec 17;2(8051):1252–1254. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92662-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. R., Gemmell C. G. Impairment by Bacteroides species of opsonisation and phagocytosis of enterobacteria. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Aug;15(3):351–361. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-3-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Onderdonk A. B., Reinap B. G., Linberg A. A. Variations of Bacteroides fragilis with in vitro passage: presence of an outer membrane-associated glycan and loss of capsular antigen. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):750–756. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. J. Aerobic and anaerobic mixtures of human pathogens: a rapid 4-plate counting technique. Br J Exp Pathol. 1977 Oct;58(5):478–483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. J. The quantitative and histological demonstration of pathogenic synergy between Escherichia coli and Bacteroides fragilis in guinea-pig wounds. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Nov;11(4):513–523. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-4-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev M., Keudell K. C., Milford A. F. Succinate as a growth factor for Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):175–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.175-178.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lykkegaard Nielsen M., Asnaes S., Justesen T. Susceptibility of the liver and biliary tract to anaerobic infection in extrahepatic biliary tract obstruction. III. Possible synergistic effect between anaerobic and aerobic bacteria. An experimental study in rabbits. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1976;11(3):263–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand D., McBride B. C. Exological relationships of bacteria involved in a simple, mixed anaerobic infection. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):44–50. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.44-50.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Louie T. J., Tally F. P., Bartlett J. G. Activity of metronidazole against Escherichia coli in experimental intra-abdominal sepsis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Mar;5(2):201–210. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Weinstein W. M., Sullivan N. M., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Experimental intra-abdominal abscesses in rats: quantitative bacteriology of infected animals. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1256–1259. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1256-1259.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. A., Skidmore A. G., Forward A. D., Clarke A. M., Sutherland E. Prospective, randomized, double-blind comparison of metronidazole and tobramycin with clindamycin and tobramycin in the treatment of intra-abdominal sepsis. Ann Surg. 1980 Aug;192(2):213–220. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198008000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tofte R. W., Peterson P. K., Schmeling D., Bracke J., Kim Y., Quie P. G. Opsonization of four Bacteroides species: role of the classical complement pathway and immunoglobulin. Infect Immun. 1980 Mar;27(3):784–792. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.3.784-792.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touw J. J., van Kampen G. P., van Steenbergen T. J., Veldhuijzen J. P., de Graaff J. The effect of culture filtrates of oral strains of black-pigmented Bacteroides on the matrix production of chick embryo cartilage cells in vitro. J Periodontal Res. 1982 Jul;17(4):351–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb01164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touw J. J., van Steenbergen T. J., De Graaff J. Butyrate: a cytotoxin for Vero cells produced by Bacteroides gingivalis and Bacteroides asaccharolyticus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1982;48(4):315–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00418285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varel V. H., Bryant M. P. Nutritional features of Bacteroides fragilis subsp. fragilis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):251–257. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.251-257.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weening R. S., Roos D., Loos J. A. Oxygen consumption of phagocytizing cells in human leukocyte and granulocyte preparations: a comparative study. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Apr;83(4):570–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein W. M., Onderdonk A. B., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Experimental intra-abdominal abscesses in rats: development of an experimental model. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1250–1255. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1250-1255.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


