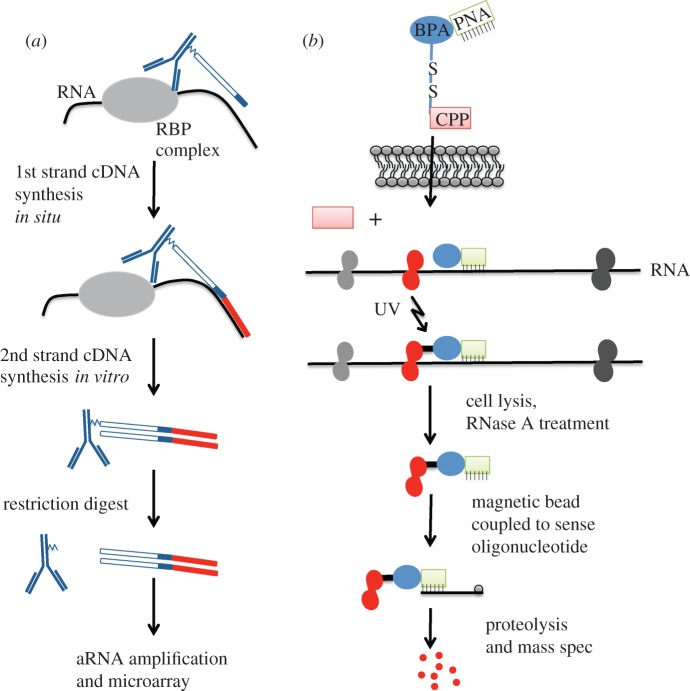
Figure 5.
Antibody-positioned amplification and PNA-assisted isolation of RNA-binding protein technologies. (a) Schematic of the APRA method. Antibodies conjugated to an oligo (blue) are applied to fixed and permeabilized cells from primary cultures. Association of the antibody with the RBP positions the oligonucleotide in close proximity to RNA interacting with the RBP. First-strand cDNA synthesis is performed in situ using a degenerate nucleotide sequence at the end of the oligo (dark blue band). Red bar indicates newly synthesized cDNA. The complexed antibody–DNA is then removed from the cells, and second strand synthesis is performed in vitro. The antibody is removed from the double-stranded DNA by restriction digest. The cDNA can then be used for aRNA amplification and microarray analysis. (b) Schematic of the PAIR method. The PAIR peptide contains a CPP (red), which allows the peptide to enter the cell. Once the cell membrane is crossed, the BPA(blue)-PNA(green) complex will dissociate from the CPP and hybridize to complementary sequence on target RNA. Application of UV irradiation cross-links the RBP (red) in near proximity to the BPA. Cells are then lysed and RNase treated. PNA–RBP complexes are isolated using sense oligonucleotides coupled to magnetic beads. This material is proteolysed and further processed for mass spectrometry.