Figure 1.
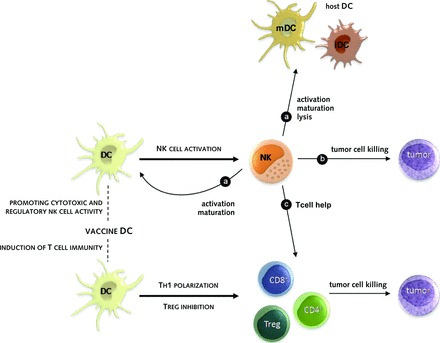
How NK cells can contribute to the antitumor efficacy of DC-based vaccination. Vaccine DCs can activate NK cells to (A) further stimulate vaccine and host DCs to advance sustained antitumor T-cell immunity, to (B) directly kill tumor cells, reducing the tumor burden and providing tumor cell material for further processing, and to (C) facilitate robust T-cell activation.
Abbreviations: iDC, immature dendritic cell; mDC, mature dendritic cell; NK, natural killer cell; Th1, T helper 1; Treg, regulatory T cell.
