Figure 6.
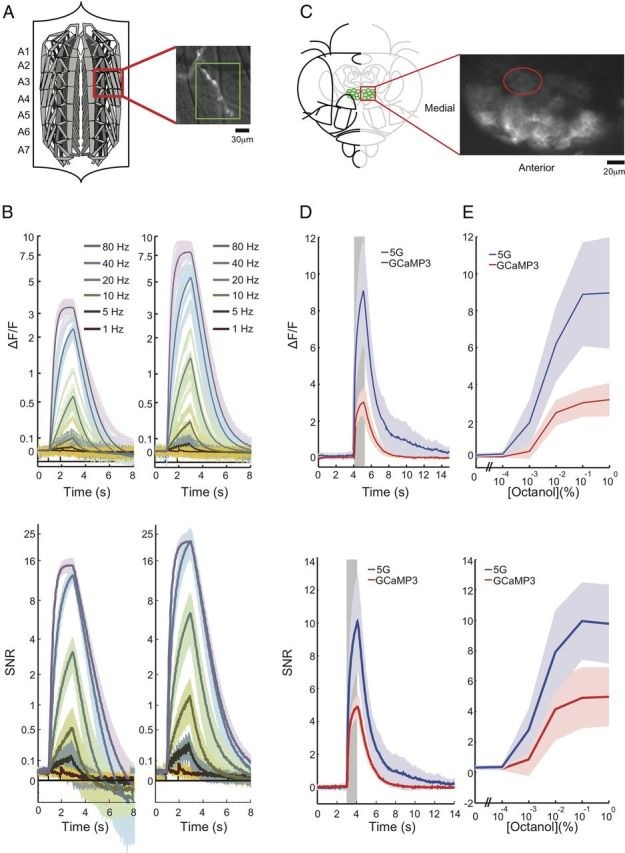
GCaMPs in Drosophila. A, Schematic of larval NMJ preparation, and close-up of Type 1b boutons from muscle 13 (segments A3–A5) used for wide-field imaging. Scale bar, 30 μm. B, Single trials of electrically evoked Ca2+ transients from wide-field imaging in the Drosophila larval NMJ. Top: Fluorescence changes (ΔF/F) traces from presynaptic terminals obtained by delivering 2 s of electrical stimulus at different frequencies. Bottom: SNR of the same data. Left, GCaMP3. Right, GCaMP5G. C, Two-photon imaging frame scan of PNs innervating the DC1 glomerulus in the adult fly AL (dorsal view) Scale bar, 20 μm. D, The mean of five replicate stimulations from six ALs (5 animals) is shown along with the SD (between AL means). Response to a 0.1% octanol, 1 s odor pulse from DC1 PNs. E, Mean octanol response from PNs from DC1 glomerulus (averaged over 5 flies) to increasing concentration. All panels show mean ± SD.
