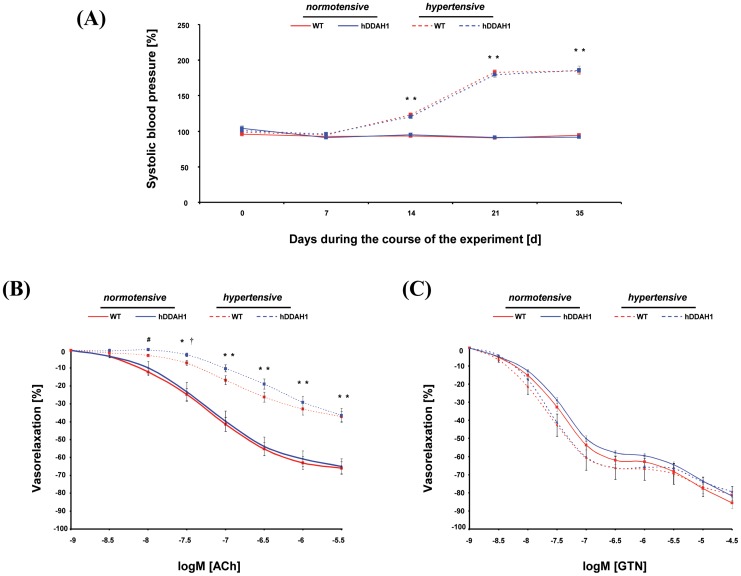
Figure 2. hDDAH1 overexpression does not significantly attenuate the increase of systolic blood pressure and the hypertension-induced impairment of endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation of aortic segments ex vivo by the combined hypertensive treatment.
(A) Systolic blood pressure during the course of the experiment. Endothelium-dependent (B) and –independent (C) relaxation of aortic segments determined by organ chamber experiments. ACh = acetylcholine, hDDAH1 = human dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase1, GTN = nitroglycerin, WT = wild-type. ACh and GTN, respectively: WT normotensive: N = 11, hDDAH1 normotensive: N = 9, WT hypertensive: N = 5, hDDAH1 hypertensive: N = 9. *p<0.01: hDDAH1 hyper- vs. normotensive and/or WT hyper- vs. normotensive. #p<0.05: hDDAH1 hyper- vs. normotensive. †p<0.05: WT hyper- vs. normotensive.