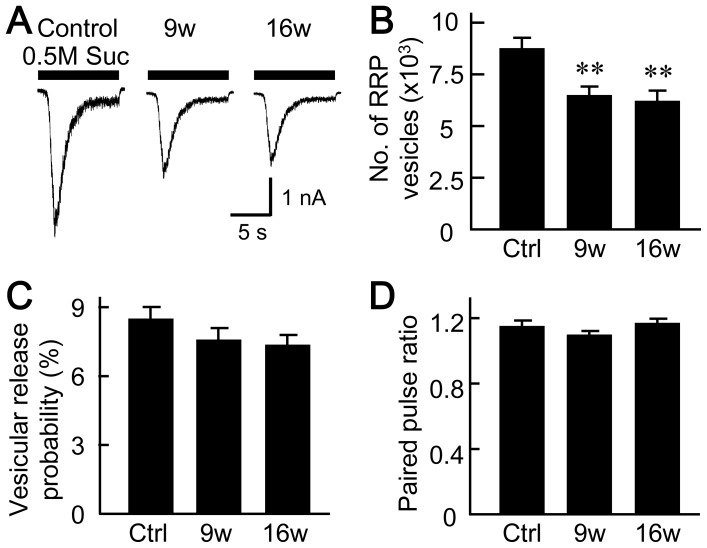
Figure 4. Astrocyte aging significantly reduces the size of the readily releasable pool of synaptic vesicles.
(A) Representative traces of the responses to 0.5 M sucrose (10 s) in autaptic neurons co-cultured with 5- (control), 9- and 16-week-old astrocytes. The response to the hypertonic sucrose solution was used to define neurotransmitter release from all vesicles in the readily releasable pool (RRP). The Vh was −70 mV. (B) Number of synaptic vesicles in RRP of autaptic neurons co-cultured with 5- (control), 9- and 16-week-old astrocytes (n = 64, 58 and 58 neurons, respectively). (C) Vesicular release probability (Pvr) in single autaptic neurons co-cultured with 5- (control), 9- and 16-week-old astrocytes (n = 80, 82 and 82 neurons, respectively). (D) Paired-pulse ratio (PPR) of evoked EPSCs. The amplitudes of EPSCs evoked by two action potentials separated by 50 ms were measured. Autaptic neurons were co-cultured with astrocytes cultured for 5- (control), 9- and 16-week (n = 64, 58 and 58 neurons, respectively). **, p<0.01.