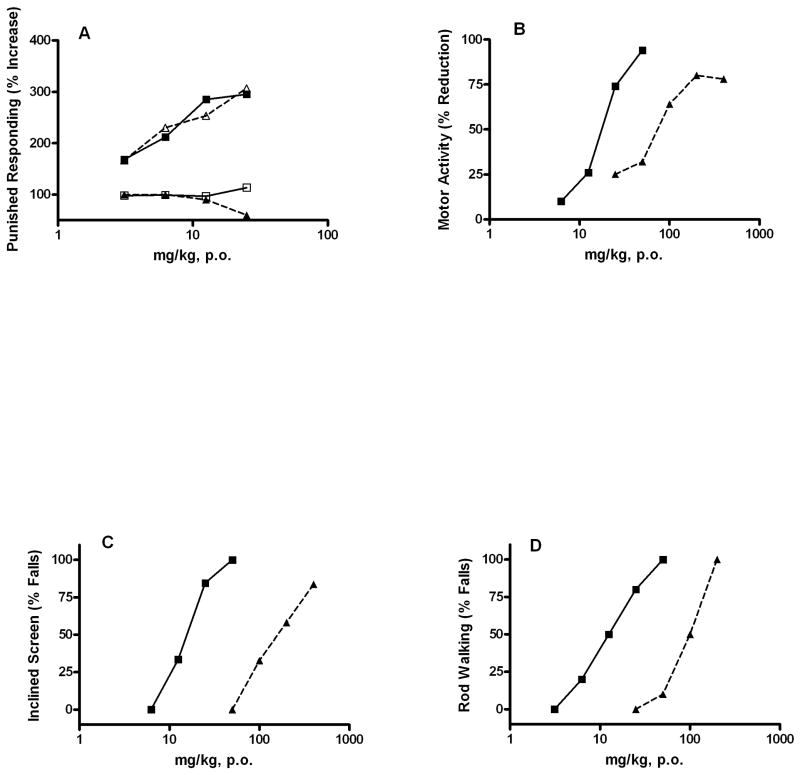
Figure 3.
Comparison of the pharmacological properties of ocinaplon and diazepam: Adult, male CD rats (Charles River) were administered vehicle, ocinaplon or diazepam by gavage. Panel A: Anticonflict actions of ocinaplon and diazepam: blockade by flumazenil. Animals were evaluated 60 min. later in the “thirsty rat conflict” test, essentially as described [31]). In brief, rats were water deprived for 48 hours and food deprived for 24 hours prior to testing. Rats were placed in the test chamber, and a 10% glucose solution made available through a stainless steel spout. After locating the spout, the rat was allowed 25 seconds of free (no shock) drinking. A circuit was then activated which applied a mild electric shock through the spout in a 5-seconds “on” 5-seconds “off” schedule for 5 minutes. The number of shocks delivered (the animal must be in contact with the spout to receive a shock) is recorded. Parallel groups received flumazenil (12.5 mg/kg, i.p.) 30 min. prior to testing. This dose of flumazenil does not affect performance in the thirsty rat conflict test (data not shown). The minimum effective dose (MED; the first dose producing a statistically significant difference from vehicle treated rats) of ocinaplon and diazepam was 3.1 mg/kg. Values represent the mean (n ≥ 8 animals/dose) % increase in punished responding compared to vehicle treated rats. Symbols: open triangles, ocinaplon; closed squares, diazepam; closed triangles, ocinaplon+flumazenil; open squares squares: diazepam+flumazenil.
Panel B: Effects of ocinaplon and diazepam on motor activity in rats. Compounds were evaluated 60 minutes after oral administration. Values represent the mean % decrease in motor activity of 12–24 rats/dose compared to vehicle treated animals. The ED50 of diazepam and ocinaplon was 17.5 and 81.7 mg/kg, respectively. Symbols: Open triangles, ocinaplon; closed squares, diazepam.
Panel C: Effects of ocinaplon and diazepam on the inclined screen: The effect of diazepam and ocinaplon was evaluated on the ability of rats to remain on an inclined (60°) screen for 30 min. The ED50 of diazepam and ocinaplon was 15.5 (3.5–24.9, 95% C.I.) and 172.2 (123.3–244.5, 95% C.I.) mg/kg, respectively. Symbols as in Panel B.
Panel D: Effects of ocinaplon and diazepam on rod walking: Animals were trained to traverse a rod inclined at 17°. Values represent the mean of 10 rats/dose. The ED50 of diazepam and ocinaplon was 13.8 (2.7–20.4, 95% C.I.) and 92 (68–124, 95% C.I.) mg/kg, respectively. Symbols: as in Panel B. These data are redrawn from Lippa, et al. [30].