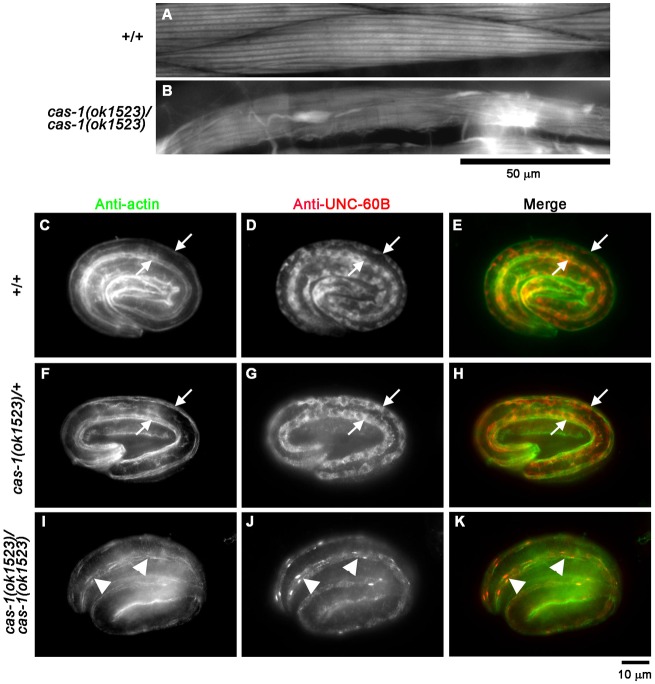
Fig. 7.
cas-1 mutation causes disorganization of actin and UNC-60B in the body wall muscle. (A,B) F-actin organization in late larval body wall muscle. Wild-type (+/+; A) or cas-1(ok1523) homozygous (cas-1(ok1523)/cas-1(ok1523); B) worms were stained with tetramethylrhodamine–phalloidin, and regions of the body wall muscle are shown. Scale bar: 50 µm. (C–K) Localization of UNC-60B and actin in embryos. Wild-type (+/+; C–E), cas-1 heterozygous (cas-1(ok1523)/+; F–H) or cas-1 homozygous (cas-1(ok1523)/cas-1(ok1523); I–K) embryos were fixed and immunostained for actin (C,F,I) and UNC-60B (D,G,J). Merged images are shown in E, H and K (actin in green and UNC-60B in red). Arrows in C–H indicate positions of the body wall muscle. Arrowheads in I–K indicate abnormal aggregates of actin and UNC-60B.