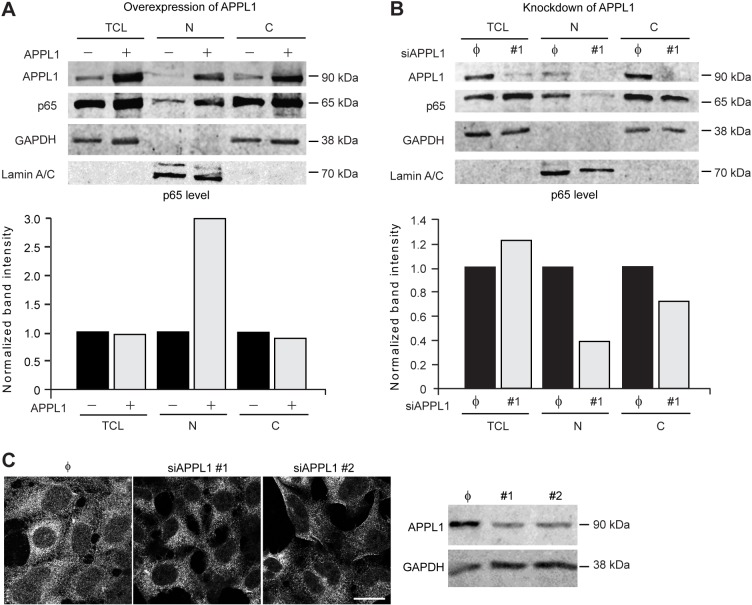
Fig. 4.
APPL1 induces nuclear accumulation of p65. (A) APPL1 overexpression induces translocation of p65 to the nucleus. HEK293T cells were transfected with APPL1-expressing vector or empty vector as a control. Forty-eight hours after transfection total cell lysate (TCL), cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) fractions were analyzed by western blotting with anti-APPL1, -p65, -GAPDH and -lamin-A/C antibodies (upper panel), and the intensity of the p65 band was quantified (lower panel). A representative result from four independent experiments is shown. (B) APPL1 knockdown prevents nuclear accumulation of p65. HEK293T cells were transfected with APPL1 siRNA #1 or non-targeting siRNA (φ). Forty-eight hours after transfection the cell fractions were prepared and analyzed as in A. (C) Immunofluorescence microscopy confirms inhibition of translocation of p65 to the nucleus upon APPL1 knockdown. Forty-eight hours after transfection with non-targeting siRNA (φ) or APPL1 siRNAs (#1 or #2), HEK293T cells were fixed and stained with anti-p65 antibody (left panel). Scale bar: 20 µm. Knockdown of APPL1 level was confirmed by immunoblotting (right panel) with GAPDH level as a loading control.