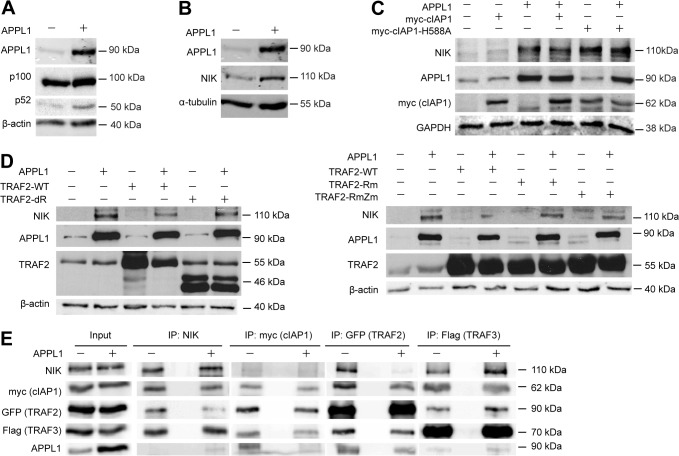
Fig. 6.
APPL1 stabilizes NIK. (A) APPL1 overexpression promotes p100 processing to p52. HEK293T cells were transfected with APPL1-expression vector or an empty vector for 48 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by western blotting for APPL1, p100, p52 and β-actin (loading control). (B) APPL1 overexpression regulates NIK protein level. The levels of APPL1, NIK and α-tubulin (loading control) were analyzed by western blotting upon APPL1 overexpression for 48 h. (C) APPL1 overexpression stabilizes NIK. HEK293T cells were transfected with APPL1, myc–cIAP1 and myc–cIAP1-H588A expression vectors either alone or in combination. The levels of APPL1, NIK, myc (cIAP1) and GAPDH (loading control) were analyzed 48 h after transfection. (D) E3 ligase-deficient TRAF2 mutants do not affect APPL1-induced NIK stability. HEK293T cells were transfected with APPL1, TRAF2, TRAF2-Rm, TRAF2-RmZm and TRAF2-dR expression vectors either alone or in combination. The levels of APPL1, NIK, TRAF2 and β-actin (loading control) were analyzed by western blotting 48 h after transfection. (E) APPL1 overexpression modulates the composition of the NIK degradative complex. Cell lysate from HEK293T cells transfected with NIK, myc–cIAP1, GFP–TRAF2, Flag–TRAF3 together with or without APPL1 were subjected to coimmunoprecipitation with rabbit anti-NIK, anti-myc, anti-GFP or mouse anti-Flag antibodies. Input represents 10% of total cell lysate used for immunoprecipitation.