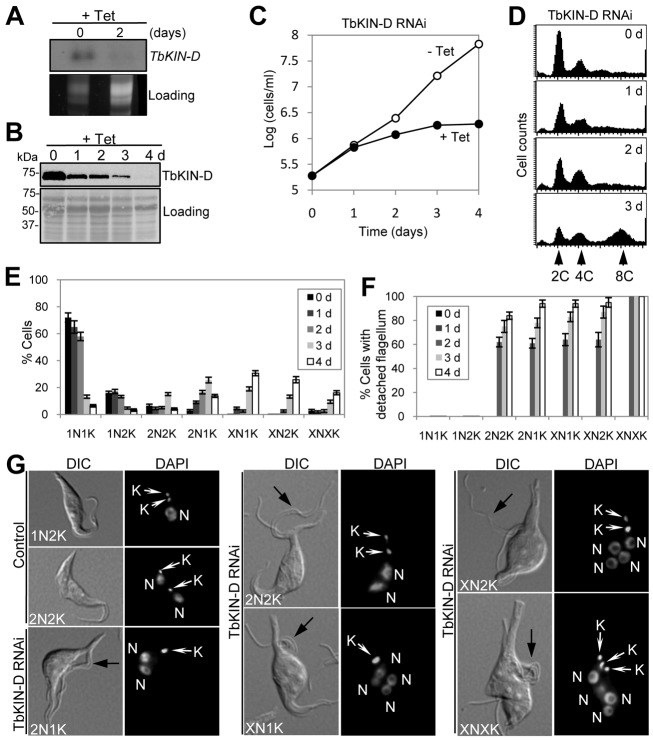
Fig. 2.
RNAi of TbKIN-D in the procyclic form of T. brucei inhibits cell proliferation. (A) TbKIN-D mRNA level in control and RNAi-treated cells, detected by northern blotting. (B) TbKIN-D protein level in control and RNAi-treated cells, detected by western blotting with anti-HA antibody. (C) RNAi of TbKIN-D resulted in growth inhibition and cell death. (D) Flow cytometry analysis of TbKIN-D RNAi cells. (E). Tabulation of cells with different numbers of nuclei (N) and kinetoplasts (K) upon TbKIN-D knockdown. (F) Percentage of TbKIN-D RNAi cells with a detached flagellum. (G) Morphology of TbKIN-D RNAi cells. Black arrows indicate the detached flagellum in TbKIN-D RNAi cells. N, nucleus; K, kinetoplast.