Fig. 3.
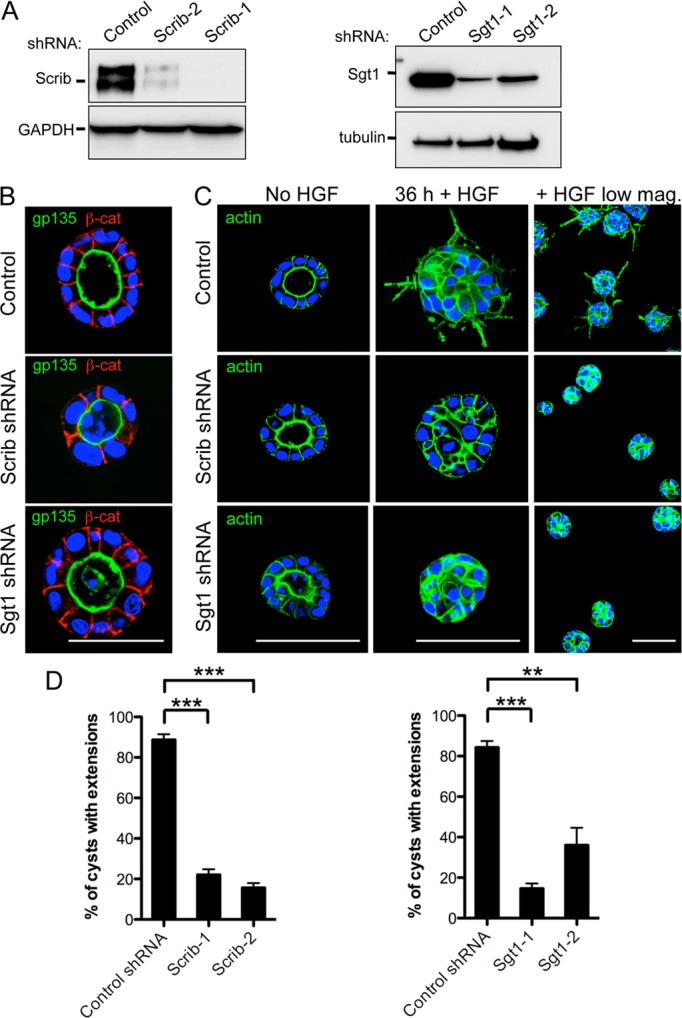
Reduction of Scrib or Sgt1 protein levels blocks HGF-mediated extension formation. (A) Western blot of MDCK total cell lysates treated with either a control shRNA or shRNAs directed against Scrib or Sgt1. GAPDH was included as a loading control for the lysates. (B) Fixed MDCK cysts were stained with the apical domain marker gp135 and the adherens junction marker β-catenin (β-cat) as indicated. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Localization of gp135 and β-catenin is indistinguishable between control cysts and Scrib or Sgt1 RNAi cysts. (C) 4-day-old control-shRNA- or Scrib- and Sgt1-shRNA-infected cysts were induced with 50 ng/ml HGF for 36 hours followed by fixation. Actin was visualized by fluorescently labeled phalloidin staining (green) and nuclei were stained with Hoechst dye (blue). A lower magnification image of the cysts (right) provides a wider field image of the results. (D) Quantification of the HGF-induced extension formation assay results. The Y-axis represents the percentage of cysts with one or more extensions. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, Dunnett's multiple comparison test. Scale bars: 50 µm (B) and 100 µm (C).
