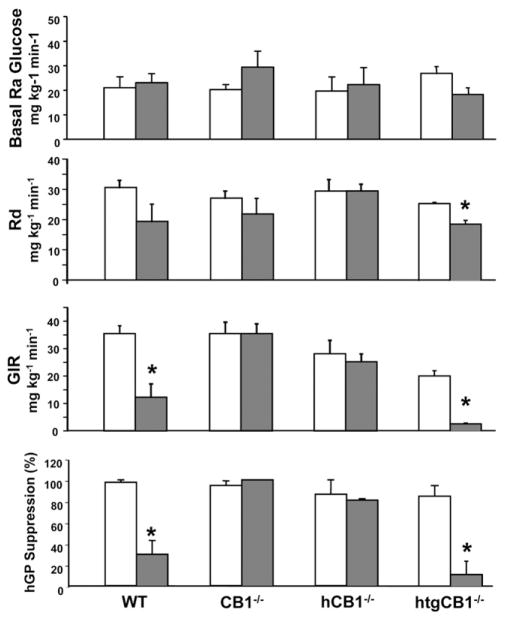
Figure 2.
HFD induces hepatic insulin resistance via activation of hepatic CB1. Hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamps were performed in wild-type, CB1−/−, hCB1−/−, and htgCB1−/− mice 5 hours after withdrawal of food, as described in Materials and Methods. The mice had been maintained on HFD (filled columns) or STD (open columns) for 14 –16 weeks before the clamps. Note that HFD results in suppression of glucose infusion rate (GIR) and hepatic glucose production (hGP), indicating decreased insulin-mediated suppression of hepatic glucose production in mice with (wild-type [WT] and htgCB1−/−) but not those without hepatic CB1 (CB1−/− or hCB1−/−). Rd, whole body glucose uptake. Means ± SE from 3– 6 animals/group are shown. *P < .05 relative to corresponding STD values.