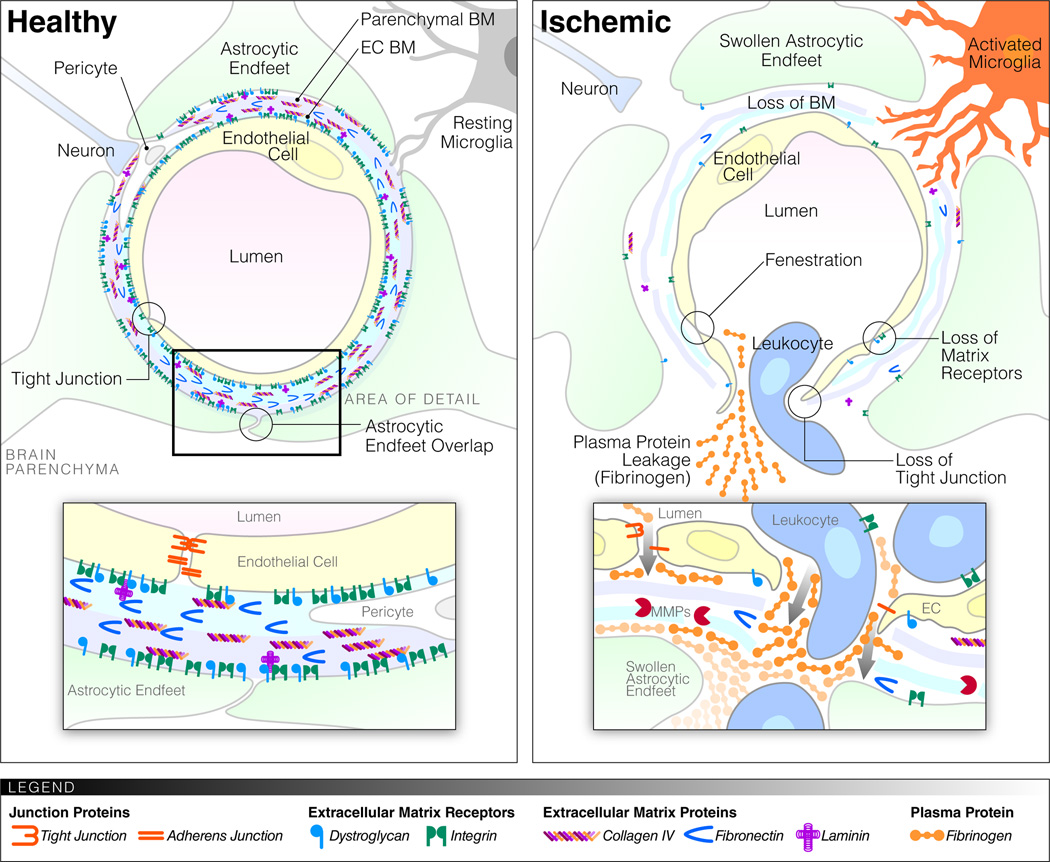
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the BBB before and after ischemia. Healthy microvessels in the brain consist of specialized ECs with TJs, their surrounding endothelial BM (blue) and astrocytic (parenchymal) BM (purple) composed of ECM proteins, and an astrocytic endfeet coverage. Cellular and matrix components of the BBB are connected through a variety of matrix receptors. Pericytes are found within the endothelial BM and occasionally the astrocytic endfeet coverage is interrupted to allow contact of microglia and neurons with the BM. After stroke/ischemia the specialized endothelial characteristics disappear, TJs are lost, fenestrations appear. The BMs become thinner and there is a marked reduction in matrix proteins and receptors. The astrocytic endfeet swell up and the contact with the vessels is lost. There is leakage of fluid, proteins and cells from the vessel lumen. Microglia become activated and might extend processes toward the blood vessels, while pericytes move away. White blood cells transmigrate via an integrin-dependent process across the endothelial BM and via an MMP-dependent process across the parenchymal BM.