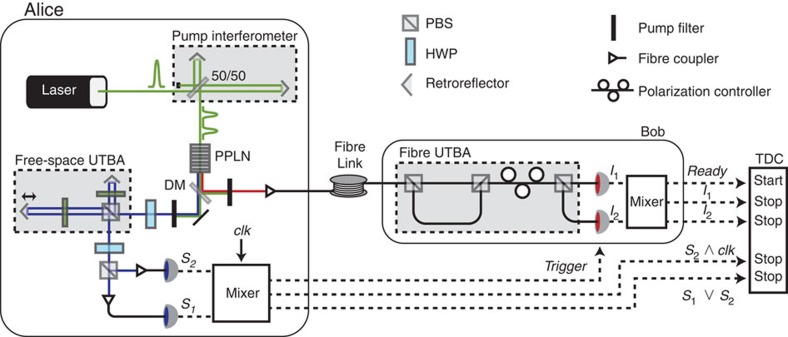
Figure 2. Experimental set-up.
A laser diode sends 50 ps pulses at 530.6 nm wavelength through an interferometer with path-length difference equivalent to 1.4-ns travel-time difference. The pulses emerge in an even superposition of two well-defined time bins that we label the early and late bins and then propagate into a nonlinear, periodically poled lithium niobate crystal (PPLN), thereby creating time-bin entangled qubits at 807 and 1,546 nm wavelengths through spontaneous parametric downconversion. The two qubits are separated at the dichroic mirror (DM). The free-space and fibre UTBAs allow Alice and Bob to measure their qubits in randomly selected bases x and y, respectively, as defined by equation (1); see Methods. The angle ϕ is selected by the orientation of the output half-wave plate (HWP) at Alice's and the polarization controller at Bob's. The coincidence detections are monitored using a TDC and analysed in real-time to realize all steps of the protocol. Clk; laser clock; PBS, polarization beam splitter.