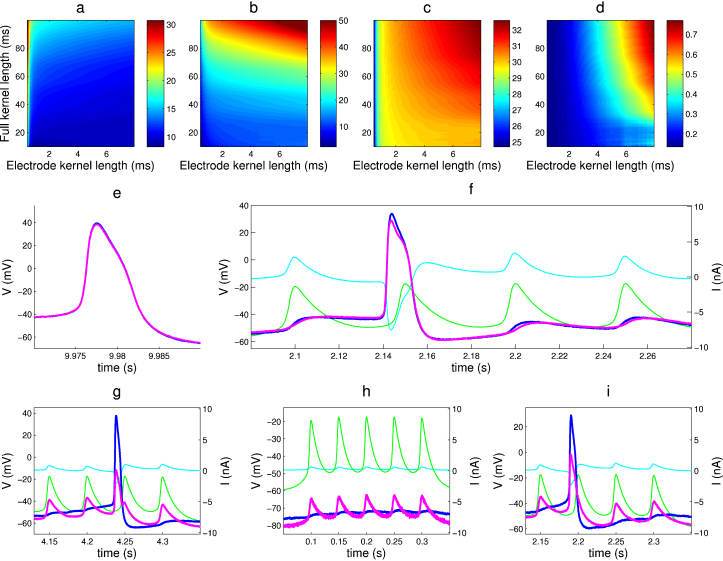
Fig. 5.
Demonstration of AEC compensation on the Lynmaea stagnalis CGC cell. (a–d) Electrode and (passive) cell membrane properties obtained from the electrode calibration results for a wide region of AEC's two most sensitive parameters (full kernel length and electrode kernel length, see Brette et al. (2008) for details). (e) Spontaneous recorded activity of the cell. (f–i) Compensation results for three investigated electrode artifact compensation techniques, while simulating a symmetric, non-rectifying gap junction synapse between StpdC's spike generator and the CGC: AEC at 100 nS (f), bridge balance at 50 nS (g) and bridge balance and capacitance neutralization combined at 20 nS (h). (i) Example of failed AEC compensation due to a too polarized electrode. Colour code: green: spike generator potential, cyan: injected current, magenta: calculated membrane potential (Vraw − Ve) in case of AEC (f and i), membrane potential as provided by the amplifier in the other cases (e, g and h), blue: control (“true”) membrane potential on an independent electrode and channel.