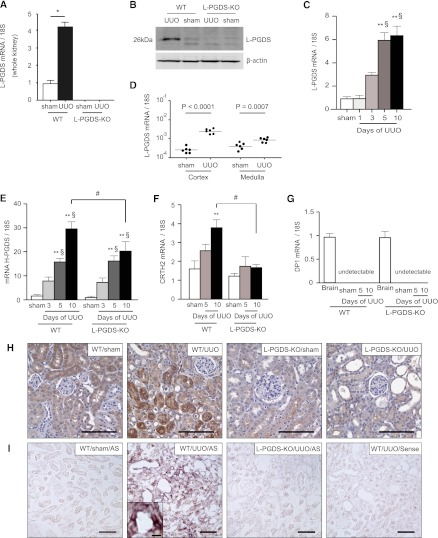
Figure 1.
L-PGDS is synthesized de novo in the tubular epithelium of kidneys from mice subjected to UUO. (A) Relative changes in L-PGDS mRNA levels in kidneys from sham-operated rats and in obstructed kidneys from WT and L-PGDS-KO 5 days after UUO (n=8 mice in each group; *P<0.001). (B) Obstructed kidneys were harvested and subjected to Western blotting with antibodies against L-PGDS and β-actin (control). (C) Time course of change in L-PGDS mRNA expression in the cortex of UUO kidneys (n=5 in each group). **P<0.05 versus sham; §P<0.05 versus day 1 (one-way ANOVA). (D) Five days after UUO, obstructed kidneys were divided macroscopically into the cortex and medulla and then subjected to quantitative RT-PCR to determine L-PGDS mRNA expression in the cortex and medulla (n=6 in each group). (E–G) Relative changes in (E) H-PGDS, (F) CRTH2, and (G) DP1 mRNA expression after UUO (n=5 in each group). Brain samples were used as a positive control. **P<0.05 versus sham (one-way ANOVA); #P<0.05 (two-sided t test); §P<0.05 versus day 1 (one-way ANOVA). Data are the mean ± SD. (H) Immunostaining for L-PGDS in the cortex 10 days after UUO or sham operation. (I) In situ hybridization of L-PGDS. Scale bars, 100 μm in H and I; 10 μm in inset.